Nutrient vitamins enabled metabolic regulation of ferroptosis via reactive oxygen species biology
- PMID: 39092216
- PMCID: PMC11291210
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1434088
Nutrient vitamins enabled metabolic regulation of ferroptosis via reactive oxygen species biology
Abstract
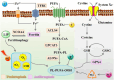
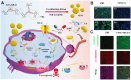
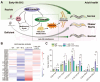
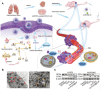
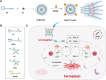
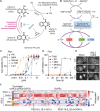
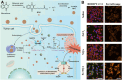
Vitamins are dietary components necessary for cellular metabolic balance, especially redox homeostasis; deficient or excessive supply may give rise to symptoms of psychiatric disorders. Exploring the nutritional and metabolic pathways of vitamins could contribute to uncovering the underlying pathogenesis of ferroptosis-associated diseases. This mini-review aims to provide insights into vitamins closely linked to the regulation of ferroptosis from the perspective of cellular reactive oxygen species biology. The mainstream reprogramming mechanisms of ferroptosis are overviewed, focusing on unique biological processes of iron metabolism, lipid metabolism, and amino acid metabolism. Moreover, recent breakthroughs in therapeutic interventions targeting ferroptosis via fully utilizing vitamin-based pharmacological tools were overviewed, covering vitamins (B, C, E, and K). Finally, mechanism insight related to vitamin-associated nutrient signaling was provided, highlighting the pharmacological benefits of metabolically reprogramming ferroptosis-associated diseases.
Keywords: ferroptosis; metabolic regulation; nutrient signaling; reactive oxygen species; vitamins.
Copyright © 2024 Wu, Shi, Zhou, Chen, Ji, Liu, Zhou, Xia, Zheng and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bao W. D., Zhou X. T., Zhou L. T., Wang F., Yin X., Lu Y., et al. (2020). Targeting miR-124/Ferroportin signaling ameliorated neuronal cell death through inhibiting apoptosis and ferroptosis in aged intracerebral hemorrhage murine model. Aging Cell 19, e13235. 10.1111/acel.13235 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

