A standardized Boswellia serrata extract shows improvements in knee osteoarthritis within five days-a double-blind, randomized, three-arm, parallel-group, multi-center, placebo-controlled trial
- PMID: 39092235
- PMCID: PMC11291344
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1428440
A standardized Boswellia serrata extract shows improvements in knee osteoarthritis within five days-a double-blind, randomized, three-arm, parallel-group, multi-center, placebo-controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Boswellin® Super is a standardized extract of Boswellia serrata Roxb gum resin, standardized to contain 30% 3-acetyl-11-keto-β-boswellic acid along with other β-boswellic acids (BSE). A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial was conducted at two doses of BSE to understand its safety and efficacy in supporting joint health and improving mobility and symptoms of osteoarthritis (OA) of the knee.
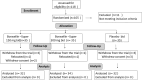
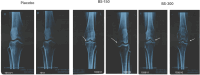
Methods: Based on the inclusion/exclusion criteria, 105 newly diagnosed participants with degenerative hypertrophy OA were recruited and randomized into Placebo, BSE-150 mg or BSE-300 mg (n = 35 in each group) to receive either 150 mg or 300 mg BSE or a placebo tablet twice a day for 90 days. All the participants were evaluated for pain and physical function using the standard tools including the Visual Analog Scale (VAS), Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC), Lequesne Functional Index (LFI), EuroQol- 5 Dimension (EQ-5D) quality of life, 6-min walk test at day 0, days 5, 30, 60 and 90 of treatment. Additionally, the circulating levels of inflammatory biomarkers, tumor necrosis factor-α (TNFα), high-sensitive C-reactive protein (hs-CRP), and interleukin-6 (IL-6) were evaluated. Safety was evaluated by blood biochemical, hematological analysis, urinary analyses and by monitoring adverse events throughout the study.
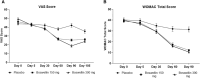
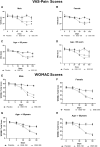
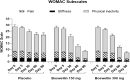
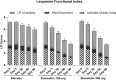
Results: Ninety-eight subjects completed the study. Improvements in pain scores were observed as early as 5 days after the start of the supplement in the BSE-150 and BSE-300 groups. By 90 days, the VAS pain score reduced by 45.3% and 61.9%, WOMAC- total score improved by 68.5% and 73.6% in the BSE-150 and BSE-300 groups respectively. WOMAC pain (70.2%, 73.9%, WOMAC stiffness (65.6%,68.9%), WOMAC function (68.8%,74.2%), LFI severity (50%,53.3%), decreased and EQ5D (56.9%, 62.9%) and distance walked in 6 minutes (21.2%, 21.9%) improved in the BSE-150 and BSE-300 groups in 90 days. Further, the levels of TNFα, hs-CRP, and IL-6 were found to decrease in the serum in BSE-supplemented participants. No significant adverse events were recorded during the study.
Conclusion: The study confirms that Boswellin® Super can be used as a safe and effective supplement to support joint health and mobility in the management of osteoarthritis.
Clinical trial registration: https://ctri.nic.in/Clinicaltrials/pmaindet2.php?EncHid=NzU2Nzc=&Enc=&userName=CTRI, identifier CTRI/2022/11/047397.
Keywords: 3-acetyl-11-keto-β-boswellic acid; Boswellia serrata extract; Boswellin Super; WOMAC; lequesne functional index quality of life; osteoarthritis; visual analog scale.
Copyright © 2024 Majeed, Majeed, Satish, Manjunatha, Rabbani, Patil and Mundkur.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors AM, GS, RM, and LM were employed by Sami-Sabinsa Group Limited. Author SM was employed by Sabinsa Corporation. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ahmed H. H., Abdel-Rahman M., Salem F. E., Shalby A., Lokman M. (2013). Antitumor efficacy of Boswellia serrata extract in management of colon cancer induced in experimental animal. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 5, 379–389.
-
- Arun Kumar M V. D. (2021). A comparison of pain and disability scores in different grades of knee OA before and after low level laser therapy (LLLT). Indian J. Clin. Anat. Physiol. 8, 60–64. 10.18231/j.ijcap.2021.014 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

