Importance of the (Pro)renin Receptor in Activating the Renin-Angiotensin System During Normotensive and Preeclamptic Pregnancies
- PMID: 39093387
- PMCID: PMC11455731
- DOI: 10.1007/s11906-024-01316-1
Importance of the (Pro)renin Receptor in Activating the Renin-Angiotensin System During Normotensive and Preeclamptic Pregnancies
Abstract
Purpose of review: For a healthy pregnancy to occur, a controlled interplay between the maternal circulating renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS), placental renin-angiotensin system (RAS) and intrarenal renin-angiotensin system (iRAS) is necessary. Functionally, both the RAAS and iRAS interact to maintain blood pressure and cardiac output, as well as fluid and electrolyte balance. The placental RAS is important for placental development while also influencing the maternal circulating RAAS and iRAS. This narrative review concentrates on the (pro)renin receptor ((P)RR) and its soluble form (s(P)RR) in the context of the hypertensive pregnancy pathology, preeclampsia.
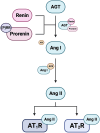
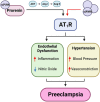
Recent findings: The (P)RR and the s(P)RR have become of particular interest as not only can they activate prorenin and renin, thus influencing levels of angiotensin II (Ang II), but s(P)RR has now been shown to directly interact with and stimulate the Angiotensin II type 1 receptor (AT1R). Levels of both placental (P)RR and maternal circulating s(P)RR are elevated in patients with preeclampsia. Furthermore, s(P)RR has been shown to increase blood pressure in non-pregnant and pregnant rats and mice. In preeclamptic pregnancies, which are characterised by maternal hypertension and impaired placental development and function, we propose that there is enhanced secretion of s(P)RR from the placenta into the maternal circulation. Due to its ability to both activate prorenin and act as an AT1R agonist, excess maternal circulating s(P)RR can act on both the maternal vasculature, and the kidney, leading to RAS over-activation. This results in dysregulation of the maternal circulating RAAS and overactivation of the iRAS, contributing to maternal hypertension, renal damage, and secondary changes to neurohumoral regulation of fluid and electrolyte balance, ultimately contributing to the pathophysiology of preeclampsia.
Keywords: (Pro)renin Receptor ((P)RR); Preeclampsia; Renin Angiotensin System (RAS).
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Placental (pro)renin receptor expression and plasma soluble (pro)renin receptor levels in preeclampsia.Placenta. 2016 Jan;37:72-8. doi: 10.1016/j.placenta.2015.11.007. Epub 2015 Nov 24. Placenta. 2016. PMID: 26684753
-
Causes and Consequences of the Dysregulated Maternal Renin-Angiotensin System in Preeclampsia.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019 Sep 10;10:563. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2019.00563. eCollection 2019. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019. PMID: 31551925 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of the human placental (pro)renin receptor-prorenin-angiotensin system by microRNAs.Mol Hum Reprod. 2018 Sep 1;24(9):453-464. doi: 10.1093/molehr/gay031. Mol Hum Reprod. 2018. PMID: 30060096
-
Unravelling soluble (pro)renin receptor-mediated endothelial dysfunction.Eur J Pharmacol. 2025 Jun 5;996:177601. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2025.177601. Epub 2025 Apr 3. Eur J Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40187599
-
Roles of collecting duct renin and (pro)renin receptor in hypertension: mini review.Ther Adv Cardiovasc Dis. 2015 Aug;9(4):191-200. doi: 10.1177/1753944715574817. Epub 2015 Mar 16. Ther Adv Cardiovasc Dis. 2015. PMID: 25780059 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lumbers ER, Pringle KG. Roles of the circulating renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in human pregnancy. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2014;306:R91–101. - PubMed
-
- Chesley LC. Hypertensive disorders in pregnancy. (Appleton-Century-Crofts, 1978).
-
- Seldin D, Giebisch G. kidney physiology and pathology, vol. 3. New York: Raven Press; 1992.
-
- Duley L. The global impact of pre-eclampsia and eclampsia. in Seminars in perinatology, Vol. 33 130–137 (Elsevier, 2009). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

