Health literacy and its associated factors among the population in two schistosomiasis-endemic villages in Jiangxi Province, China
- PMID: 39093802
- PMCID: PMC11296410
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000039107
Health literacy and its associated factors among the population in two schistosomiasis-endemic villages in Jiangxi Province, China
Abstract
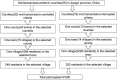
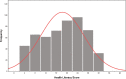
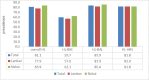
This cross-sectional study aimed to assess the levels of health literacy and the associated factors among the general population living in 2 schistosomiasis-endemic villages in Jiangxi Province, China. Multistage stratified random sampling was used to select participants, and a face-to-face survey was conducted from July to August 2021 to collect participants' socio-demographic characteristics and levels of overall health literacy (HL) and its 3 subscales: health literacy of basic knowledge and concepts (HL-BKC), health literacy of behavior and lifestyle (HL-BAL), and health literacy of health-related skills (HL-HRS). The Chi-square test and logistic regression models were used to assess the association between socio-demographic characteristics and low HL levels. The prevalence rates of low overall HL, HL-BKC, HL-BAL, and HL-HRS were 84.3%, 61.8%, 82.6%, and 86%, respectively. In addition, no significant differences (P > .05) were noted between the 2 villages regarding overall HL scores and the 3 subscales of health literacy scores. Older age (P < .001), occupation (P < .001), lower educational level (P < .001), and lower annual household income (P < .05) were associated with an increased risk of low HL. Multivariate logistic regression revealed that occupation as a student (OR = 32.289, 95% CI:1.965-530.462, P < .05) and fishermen (OR = 27.902, 95%CI:1.91-407.642, P < .05), lower education level (OR = 0.384, 95%CI:0.149-0.99, P < .05), older age (OR = 5.228, 95%CI:1.458-18.75, P < .001), and lower annual household income (OR = 0.452, 95%CI:0.24-0.851, P < .05) were independently associated with low HL. The prevalence of low HL is high among the population in the schistosomiasis-endemic villages of Jiangxi Province, China. Age, education level, occupation, and annual household income were all independent factors associated with HL levels. Health educational interventions to improve HL should be simultaneously conducted in health promotion work to reduce risky habits.
Copyright © 2024 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Health literacy and its socio-demographic risk factors in Hebei: A cross-sectional survey.Medicine (Baltimore). 2021 May 28;100(21):e25975. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000025975. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021. PMID: 34032709 Free PMC article.
-
The prevalence and related factors for low health literacy in Xingtai: A cross-sectional survey in prefecture-level city.Medicine (Baltimore). 2021 Mar 12;100(10):e24848. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000024848. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021. PMID: 33725838 Free PMC article.
-
Survey on health literacy and related factors among firefighters of emergency management departments in Southwest China.BMC Public Health. 2024 Jul 24;24(1):1983. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-19522-6. BMC Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39049012 Free PMC article.
-
Sociodemographic and health-related factors associated with low health literacy among Indigenous populations: a systematic review.Health Promot Int. 2025 Mar 5;40(2):daaf018. doi: 10.1093/heapro/daaf018. Health Promot Int. 2025. PMID: 40159950
-
Health Literacy and Physical Activity: A Systematic Review.J Phys Act Health. 2020 Oct 31;17(12):1259-1274. doi: 10.1123/jpah.2020-0161. J Phys Act Health. 2020. PMID: 33129198
References
-
- Song L-G, Wu X-Y, Sacko M, et al. . History of schistosomiasis epidemiology, current status, and challenges in China: on the road to schistosomiasis elimination. Parasitol Res. 2016;115:4071–81. - PubMed
-
- Zhang LJ, Xe JY, Yang F, et al. . [Progress of schistosomiasis control in People’s Republic of China in 2022]. Zhongguo Xue Xi Chong Bing Fang Zhi Za. 2023;35:217–224+250. - PubMed
-
- Hu GH, Hu J, Song KY, et al. . The role of health education and health promotion in the control of schistosomiasis: experiences from a 12-year intervention study in the Poyang Lake area. Acta Trop. 2005;96:232–41. - PubMed
-
- Yuan LP, Manderson L, Ren MY, et al. . School-based interventions to enhance knowledge and improve case management of schistosomiasis: a case study from Hunan, China. Acta Trop. 2005;96:248–54. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

