Influence of selected patient variables and operative blood loss on six-month survival following liver transplantation
- PMID: 3909433
- PMCID: PMC3022507
- DOI: 10.1055/s-2008-1040637
Influence of selected patient variables and operative blood loss on six-month survival following liver transplantation
Abstract
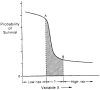
A group of 118 adults who underwent primary, orthotopic transplantation of the liver over a 4-year period served as the subjects of a detailed examination of their ability to survive the first 6 months as a function of their preoperative condition. As a result, a scoring system was developed empirically in an attempt to separate very high-risk from relatively low-risk patients. The scoring method is based on the high degree of correlation between survival probability and various patient characteristics. It allows for additional scoring to account for the dramatic effect of operative blood loss on the eventual outcome. The curve that best describes the relationship between patient scores and survival probability is sigmoidal in shape. Many patients will have scores located on the curve between the inflection points. They represent a group whose relative risk is difficult to estimate but for whom operative blood loss or the occurrence of surgical complications may prove particularly telling.
Figures



References
-
- Marquez JM, Martin DJ, Kang YG, et al. Cardiovascular depression secondary to citrate intoxication during hepatic transplantation in man. Submitted.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

