SnoRNA U50A mediates everolimus resistance in breast cancer through mTOR downregulation
- PMID: 39094511
- PMCID: PMC11342273
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tranon.2024.102062
SnoRNA U50A mediates everolimus resistance in breast cancer through mTOR downregulation
Abstract
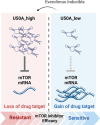
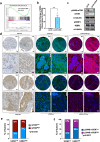
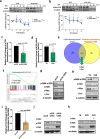
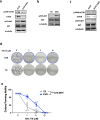
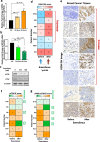
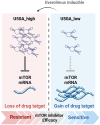
Breast cancer remains the most prevalent cancer in women globally, posing significant challenges in treatment due to the inevitable development of resistance to targeted therapies like everolimus, an mTOR inhibitor. While several mechanisms of resistance have been proposed, the role of snoRNAs in this context remains inadequately explored. Our study unveils a novel connection between snoRNAs and everolimus resistance, focusing on the snoRNA U50A. We discovered that U50A negatively regulates mTOR signaling by transcriptionally downregulating mTOR gene expression, which consequently leads to decreased sensitivity to everolimus treatment. Through RNA sequencing, gene set enrichment analyses, and experimental validations, we established that U50A overexpression in breast cancer cells results in mTOR downregulation and subsequently, everolimus desensitization. Clinical results further supported our findings, showing a higher prevalence of everolimus resistance in tumors with elevated U50A expression. Moreover, our results suggest that U50A's effect on mTOR is mediated through the suppression of the transcription factors c-Myc, with a notable impact on cancer cell viability under everolimus treatment. This study not only highlights the complex role of snoRNAs in cancer drug resistance but also proposes U50A as a potential biomarker for predicting everolimus efficacy in breast cancer treatment.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Drug resistance; Everolimus; U50A; mTOR; snoRNAs.
Copyright © 2024. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

