Hybrid immunity to SARS-CoV-2 arises from serological recall of IgG antibodies distinctly imprinted by infection or vaccination
- PMID: 39094579
- PMCID: PMC11384961
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2024.101668
Hybrid immunity to SARS-CoV-2 arises from serological recall of IgG antibodies distinctly imprinted by infection or vaccination
Abstract
We describe the molecular-level composition of polyclonal immunoglobulin G (IgG) anti-spike antibodies from ancestral severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection, vaccination, or their combination ("hybrid immunity") at monoclonal resolution. Infection primarily triggers S2/N-terminal domain (NTD)-reactive antibodies, whereas vaccination mainly induces anti-receptor-binding domain (RBD) antibodies. This imprint persists after secondary exposures wherein >60% of ensuing hybrid immunity derives from the original IgG pool. Monoclonal constituents of the original IgG pool can increase breadth, affinity, and prevalence upon secondary exposures, as exemplified by the plasma antibody SC27. Following a breakthrough infection, vaccine-induced SC27 gained neutralization breadth and potency against SARS-CoV-2 variants and zoonotic viruses (half-maximal inhibitory concentration [IC50] ∼0.1-1.75 nM) and increased its binding affinity to the protective RBD class 1/4 epitope (dissociation constant [KD] < 5 pM). According to polyclonal escape analysis, SC27-like binding patterns are common in SARS-CoV-2 hybrid immunity. Our findings provide a detailed molecular definition of immunological imprinting and show that vaccination can produce class 1/4 (SC27-like) IgG antibodies circulating in the blood.
Keywords: COVID-19; Ig-seq; SARS-CoV-2; antibody feedback; bNAb; broadly neutralizing monoclonal antibody; cryo-EM; hybrid immunity; immunological imprinting; plasma.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests R.S.B. is a member of advisory boards for Vaxart, Takeda, and Invivyd and has collaborative projects with Gilead, J&J, and HilleVax, focused on unrelated projects. S.R.L. and R.S.B. are co-inventors of methods and uses of mouse-adapted SARS-CoV-2 viruses (US patent US11225508B1). J.D.B. is on the scientific advisory boards of Apriori Bio, Invivyd, Aerium Therapeutics, and the Vaccine Company. J.D.B. and B.D. are inventors on Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center-licensed patents related to viral deep mutational scanning. R.S.B., G.G., W.N.V., J.J.L., and G.C.I. are inventors on a provisional US patent application for mAb SC27 and other new antibodies described in this manuscript, entitled “Broadly neutralizing human monoclonal antibodies that target the SARS-CoV-2 receptor binding domain (RBD)” (63/491,270).
Figures
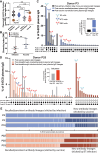
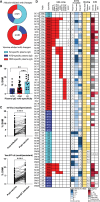

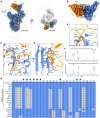
Update of
-
Hybrid immunity to SARS-CoV-2 arises from serological recall of IgG antibodies distinctly imprinted by infection or vaccination.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jan 23:2024.01.22.576742. doi: 10.1101/2024.01.22.576742. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Cell Rep Med. 2024 Aug 20;5(8):101668. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2024.101668. PMID: 38545622 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Amanat F., Thapa M., Lei T., Ahmed S.M.S., Adelsberg D.C., Carreño J.M., Strohmeier S., Schmitz A.J., Zafar S., Zhou J.Q., et al. SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination induces functionally diverse antibodies to NTD, RBD, and S2. Cell. 2021;184:3936–3948.e10. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.06.005. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

