The stroke outcome optimization project: Acute ischemic strokes from a comprehensive stroke center
- PMID: 39095364
- PMCID: PMC11297183
- DOI: 10.1038/s41597-024-03667-5
The stroke outcome optimization project: Acute ischemic strokes from a comprehensive stroke center
Abstract
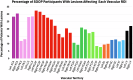
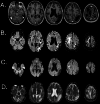
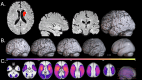
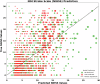
Stroke is a leading cause of disability, and Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is routinely acquired for acute stroke management. Publicly sharing these datasets can aid in the development of machine learning algorithms, particularly for lesion identification, brain health quantification, and prognosis. These algorithms thrive on large amounts of information, but require diverse datasets to avoid overfitting to specific populations or acquisitions. While there are many large public MRI datasets, few of these include acute stroke. We describe clinical MRI using diffusion-weighted, fluid-attenuated and T1-weighted modalities for 1715 individuals admitted in the upstate of South Carolina, of whom 1461 have acute ischemic stroke. Demographic and impairment data are provided for 1106 of the stroke survivors from this cohort. Our validation demonstrates that machine learning can leverage the imaging data to predict stroke severity as measured by the NIH Stroke Scale/Score (NIHSS). We share not only the raw data, but also the scripts for replicating our findings. These tools can aid in education, and provide a benchmark for validating improved methods.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Writing Group Members. et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2016 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation133, e38–360 (2016). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- P50 DC014664/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 MH133701/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- RF1MH133701/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH)
- P50DC014664/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders (NIDCD)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

