A systematic review assessing the association of inflammatory markers with kidney dysfunction in people living with HIV on highly active antiretroviral therapy
- PMID: 39095687
- PMCID: PMC11297709
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-024-09594-5
A systematic review assessing the association of inflammatory markers with kidney dysfunction in people living with HIV on highly active antiretroviral therapy
Abstract
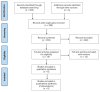
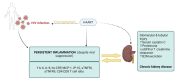
Monitoring chronic diseases, particularly kidney disorders, in people living with HIV (PLWH) is of paramount importance. Here, a systematic search was conducted across electronic search engine and databases like PubMed, Scopus, and Google Scholar, from date of inception until December 2023, to identify pertinent studies reporting on any association between inflammation and kidney function in PLWH. Only six clinical studies in peer-reviewed journals met the inclusion criteria, involving 1467 participants aged 37 to 51, with approximately 17% being females. The report emphasizes the potential impact of highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) on kidney function in PLWH, highlighting the significance of monitoring inflammation markers as indicators of kidney function, even when HAART is effective. Acknowledging study limitations, particularly the scarcity of relevant research, the findings highlight a need for more research to inform on clinical guidance to optimize HIV management, particularly regarding kidney health and HAART regimens. Although very limited studies were evaluated, the study lays an important foundation for future research to uncover the complex relationship between HAART, inflammation markers, and kidney health in PLWH.
Keywords: HIV; Highly active antiretroviral therapy; Inflammation; Kidney disease; Prognosis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

