Adipocyte endothelin B receptor activation inhibits adiponectin production and causes insulin resistance in obese mice
- PMID: 39096077
- PMCID: PMC11421981
- DOI: 10.1111/apha.14214
Adipocyte endothelin B receptor activation inhibits adiponectin production and causes insulin resistance in obese mice
Erratum in
-
Correction to "Adipocyte endothelin B receptor activation inhibits adiponectin production and causes insulin resistance in obese mice".Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2025 Jun;241(6):e70061. doi: 10.1111/apha.70061. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2025. PMID: 40411248 No abstract available.
Abstract
Aims: Endothelin-1 (ET-1) is elevated in patients with obesity and adipose tissue of obese mice fed high-fat diet (HFD); however, its contribution to the pathophysiology of obesity is not fully understood. Genetic loss of endothelin type B receptors (ETB) improves insulin sensitivity in rats and leads to increased circulating adiponectin, suggesting that ETB activation on adipocytes may contribute to obesity pathophysiology. We hypothesized that elevated ET-1 in obesity promotes insulin resistance by reducing the secretion of insulin sensitizing adipokines, via ETB receptor.
Methods: Male adipocyte-specific ETB receptor knockout (adETBKO), overexpression (adETBOX), or control littermates were fed either normal diet (NMD) or high-fat diet (HFD) for 8 weeks.
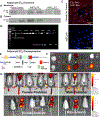
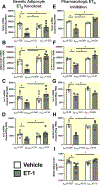
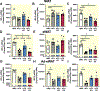
Results: RNA-sequencing of epididymal adipose (eWAT) indicated differential expression of over 5500 genes (p < 0.05) in HFD compared to NMD controls, and changes in 1077 of these genes were attenuated in HFD adETBKO mice. KEGG analysis indicated significant increase in metabolic signaling pathway. HFD adETBKO mice had significantly improved glucose and insulin tolerance compared to HFD control. In addition, adETBKO attenuated changes in plasma adiponectin, insulin, and leptin that is observed in HFD versus NMD control mice. Treatment of primary adipocytes with ET-1 caused a reduction in adiponectin production that was attenuated in cells pretreated with an ETB antagonist.
Conclusion: These data indicate elevated ET-1 in adipose tissue of mice fed HFD inhibits adiponectin production and causes insulin resistance through activation of the ETB receptor on adipocytes.
Keywords: adipocytes; endothelin‐1; insulin sensitivity; obesity.
© 2024 Scandinavian Physiological Society. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





References
-
- Apovian CM. Obesity: definition, comorbidities, causes, and burden. Am J Manag Care. 2016;22(7 Suppl):s176–85. - PubMed
-
- Dimitriadis G, Mitrou P, Lambadiari V, Maratou E, Raptis SA. Insulin effects in muscle and adipose tissue. Diabetes research and clinical practice. 2011;93:S52–S9. - PubMed
-
- Miller RA, Chu Q, Le Lay J, Scherer PE, Ahima RS, Kaestner KH, Foretz M, Viollet B, Birnbaum MJ. Adiponectin suppresses gluconeogenic gene expression in mouse hepatocytes independent of LKB1-AMPK signaling. J Clin Invest. 2011;121(6):2518–28. Epub 2011/05/25. doi: 10.1172/JCI45942. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mukherjee S, Chattopadhyay M, Bhattacharya S, Dasgupta S, Hussain S, Bharadwaj SK, Talukdar D, Usmani A, Pradhan BS, Majumdar SS, Chattopadhyay P, Mukhopadhyay S, Maity TK, Chaudhuri MK, Bhattacharya S. A Small Insulinomimetic Molecule Also Improves Insulin Sensitivity in Diabetic Mice. PLoS One. 2017;12(1):e0169809. Epub 2017/01/11. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0169809. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

