The amalgam of naive CD4+ T cell transcriptional states is reconfigured by helminth infection to dampen the amplitude of the immune response
- PMID: 39096910
- PMCID: PMC11421571
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2024.07.006
The amalgam of naive CD4+ T cell transcriptional states is reconfigured by helminth infection to dampen the amplitude of the immune response
Abstract
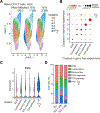
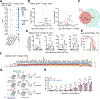
Naive CD4+ T cells in specific pathogen-free (SPF) mice are characterized by transcriptional heterogeneity and subpopulations distinguished by the expression of quiescence, the extracellular matrix (ECM) and cytoskeleton, type I interferon (IFN-I) response, memory-like, and T cell receptor (TCR) activation genes. We demonstrate that this constitutive heterogeneity, including the presence of the IFN-I response cluster, is commensal independent insofar as being identical in germ-free and SPF mice. By contrast, Nippostrongylus brasiliensis infection altered this constitutive heterogeneity. Naive T cell-intrinsic transcriptional changes acquired during helminth infection correlated with and accounted for decreased immunization response to an unrelated antigen. These compositional and functional changes were dependent variables of helminth infection, as they disappeared at the established time point of its clearance in mice. Collectively, our results indicate that the naive T cell pool is subject to dynamic transcriptional changes in response to certain environmental cues, which in turn permutes the magnitude of the immune response.
Keywords: T cells; commensal microbiota; helminth; naive T cell; transcriptional heterogeneity; vaccines.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests Z.E. is currently a medical student at the University of North Dakota; A.P.M. is a postdoctoral fellow at McGill University; D.A.d.K. is currently a resident at the University of California, San Diego; and Y.W. is currently a postdoctoral fellow at St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital.
Figures




Comment in
-
Wriggly woes: Helminths stirring up T cell trouble.Immunity. 2024 Aug 13;57(8):1726-1728. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2024.07.014. Immunity. 2024. PMID: 39142272
References
-
- Aguirre-Gamboa R, Joosten I, Urbano PCM, van der Molen RG, van Rijssen E, van Cranenbroek B, Oosting M, Smeekens S, Jaeger M, Zorro M, et al. (2016). Differential Effects of Environmental and Genetic Factors on T and B Cell Immune Traits. Cell Rep 17, 2474–2487. 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.10.053. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

