Neuromodulation modifies α-synuclein spreading dynamics in vivo and the pattern is predicted by changes in whole-brain function
- PMID: 39096960
- PMCID: PMC11416857
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brs.2024.07.021
Neuromodulation modifies α-synuclein spreading dynamics in vivo and the pattern is predicted by changes in whole-brain function
Abstract
Background: Many neurodegenerative disease treatments, such as deep brain stimulation for Parkinson's Disease, can alleviate symptoms by primarily compensating for circuit dysfunctions. However, the stimulation's effect on the underlying disease progression remains relatively unknown. Here, we report that neuromodulation can not only modulate circuit function but also modulate the in vivo spreading dynamics of α-synuclein pathology, the primary pathological hallmark observed in Parkinson's Disease.
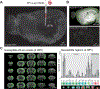
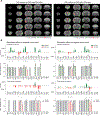
Methods: In a mouse model, pre-formed fibrils were injected into the striatum to induce widespread α-synuclein pathology. Two days after fibril injection, mice were treated for two weeks with daily optogenetic stimulation of the Secondary Motor Area, Layer V. Whole brains were then extracted, immunolabeled, cleared, and imaged with light-sheet fluorescent microscopy.
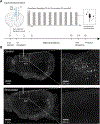
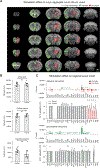
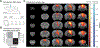
Results: Repeated optogenetic stimulation led to a decrease in pathology at the site of stimulation and at various cortical and subcortical regions, while the contralateral cortex saw a consistent increase. Aligning the pathology changes with optogenetic-fMRI measured brain activity, we found that the changes in pathology and brain function had similar spatial locations but opposite polarity.
Conclusion: These results demonstrate the ability to modulate and predict whole brain pathology changes using neuromodulation, opening a new horizon for investigating optimized neuromodulation therapies.
Keywords: Circuit function; Neuromodulation; Optogenetics; Parkinson's disease; α-Synuclein.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest J.H.L. is a founder, consultant, and board member of LVIS. The rest of the authors declare no potential conflicts of interest. None of the funding sources played a role in the design, collection, analysis, interpretation of the data, or in the decision to submit the manuscript for publication.
Figures
References
-
- Goedert M, Spillantini MG, Del Tredici K, Braak H. 100 years of Lewy pathology. Nat Rev Neurol 2013;9(1):13–24. - PubMed
-
- Braak H, Del Tredici K, Bratzke H, Hamm-Clement J, Sandmann-Keil D, Rub U. Staging of the intracerebral inclusion body pathology associated with idiopathic Parkinson’s disease (preclinical and clinical stages). J Neurol 2002;249 Suppl 3:III/1–5. - PubMed
-
- Braak H, Del Tredici K, Rub U, de Vos RA, Jansen Steur EN, Braak E. Staging of brain pathology related to sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 2003;24(2):197–211. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

