Enzalutamide inhibits PEX10 function and sensitizes prostate cancer cells to ROS activators
- PMID: 39097593
- PMCID: PMC11297951
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-024-06937-7
Enzalutamide inhibits PEX10 function and sensitizes prostate cancer cells to ROS activators
Abstract
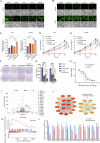
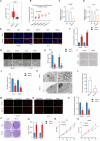
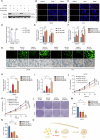
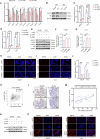
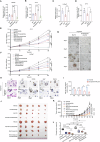
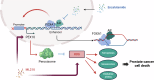
Sharply increased reactive oxygen species (ROS) are thought to induce oxidative stress, damage cell structure and cause cell death; however, its role in prostate cancer remains unclear. Enzalutamide is a widely used anti-prostate cancer drug that antagonizes androgen binding with its receptor. Further exploration of the mechanism and potential application strategies of enzalutamide is crucial for the treatment of prostate cancer. Here, we confirmed PEX10 can be induced by ROS activators while reduce ROS level in prostate cancer cells, which weakened the anti-tumor effect of ROS activators. The androgen receptor (AR) can promote the expression of PEX10 by acting as an enhancer in cooperation with FOXA1. The anti-tumor drug enzalutamide inhibits PEX10 by inhibiting the function of AR, and synergize with ROS activators ML210 or RSL3 to produce a stronger anti-tumor effect, thereby sensitizing cells to ROS activators. This study reveals a previously unrecognized function of enzalutamide and AR by regulating PEX10 and suggests a new strategy of enzalutamide application in prostate cancer treatment.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

