Proteomics and machine learning in the prediction and explanation of low pectoralis muscle area
- PMID: 39097658
- PMCID: PMC11297919
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-68447-y
Proteomics and machine learning in the prediction and explanation of low pectoralis muscle area
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Proteomics and machine learning in the prediction and explanation of low pectoralis muscle area.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 4;15(1):7613. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-87597-1. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40038365 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Low muscle mass is associated with numerous adverse outcomes independent of other associated comorbid diseases. We aimed to predict and understand an individual's risk for developing low muscle mass using proteomics and machine learning. We identified eight biomarkers associated with low pectoralis muscle area (PMA). We built three random forest classification models that used either clinical measures, feature selected biomarkers, or both to predict development of low PMA. The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve for each model was: clinical-only = 0.646, biomarker-only = 0.740, and combined = 0.744. We displayed the heterogenetic nature of an individual's risk for developing low PMA and identified two distinct subtypes of participants who developed low PMA. While additional validation is required, our methods for identifying and understanding individual and group risk for low muscle mass could be used to enable developments in the personalized prevention of low muscle mass.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Mr. Enzer reports no conflicts of interest. Dr. Mason reports employment by Sarepta Therapeutics, outside of this current work, and grant funding from the National Institutes of Health (NIH), related to this current work. Dr. Chiles reports grant funding from the NIH. Dr. McDonald reports no conflicts of interest. Dr. Shirahata reports no conflicts of interest. Ms. Yuan reports no conflicts of interest. Mr. Castro reports no conflicts of interest. Dr. Regan reports no conflicts of interest. Dr. Choi reports consulting fees from Quantitative Imaging Solutions, outside of this current work. Dr. Diaz reports no conflicts of interest. Dr Washko reports ownership/dividend from Quantitative Imaging Solutions, outside of this current work. Dr. Estépar reports ownership/dividend from Quantitative Imaging Solutions, outside of this current work. Dr. Ash reports ownership/dividend from Quantitative Imaging Solutions, outside of this current work, and grant funding from the National Institutes of Health (NIH), related to this current work. The COPDGene study consortium (NCT00608764) is supported by NHLBI U01 HL089897 and U01 HL089856, as well as by the COPD Foundation through contributions made to an Industry Advisory Board comprised of AstraZeneca, Bayer Pharmaceuticals, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Genentech, GlaxoSmithKline, Novartis, Pfizer, and Sunovion. The remaining authors do not have any competing interests to declare.
Figures


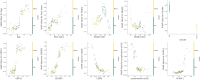

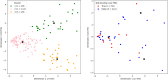
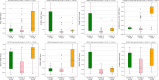
Update of
-
Proteomics and Machine Learning in the Prediction and Explanation of Low Pectoralis Muscle Area.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2024 Mar 4:rs.3.rs-3957125. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-3957125/v1. Res Sq. 2024. Update in: Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 3;14(1):17981. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-68447-y. PMID: 38496412 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01HL089897/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007633/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL116931/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL089856/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL105346/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL116931/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL149861/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL122464/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL153460/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32HL007633/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K08HL145118/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL164824/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- L70 HL165665/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL089897/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL173017/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 HL145118/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32HL105346/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

