Patient-reported symptoms and burden of eosinophilic esophagitis: evidence from real-world clinical practice
- PMID: 39097693
- PMCID: PMC11297626
- DOI: 10.1186/s12876-024-03334-4
Patient-reported symptoms and burden of eosinophilic esophagitis: evidence from real-world clinical practice
Abstract
Background: Eosinophilic esophagitis is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the esophagus. This real-world study used patient and physician surveys to describe the clinical characteristics and disease burden of eosinophilic esophagitis-overall and in a subgroup of patients with dysphagia despite treatment.
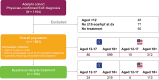
Methods: Data analyzed in this study were collected in 2020 from US and EU patients with eosinophilic esophagitis. Eligible patients were aged ≥ 12 years with a diagnosis of eosinophilic esophagitis, had an esophageal count of ≥ 15 eosinophils/high-power field at diagnosis, and were currently prescribed treatment for eosinophilic esophagitis.
Results: Overall, 1001 patients were included, of whom 356 (36%) had dysphagia despite treatment. Demographics and clinical characteristics were similar in both populations. The severity of eosinophilic esophagitis was mild in more patients overall (69%) versus those with dysphagia despite treatment (48%). Patient disease history was similar in both populations, with some exceptions: common patient-reported symptoms were dysphagia (70% and 86%) and heartburn/acid reflux (55% and 49%), and common physician-reported symptoms were dysphagia (75% and 91%) and food impaction (46% and 52%). Treatment history was similar in both populations; overall, the most common treatments were proton pump inhibitors (83%) and topical corticosteroids (51%). Patients reported slightly more days with symptoms, higher impacts on activities of daily living, and slightly higher anxiety or depression in the dysphagia-despite-treatment population versus the overall population.
Conclusions: Eosinophilic esophagitis presents severe symptoms and comorbidities that substantially impact patients' well-being and quality of life. Greater awareness of and novel treatments for eosinophilic esophagitis are needed.
Keywords: Disease burden; Eosinophilic esophagitis; Health-related quality of life; Inflammatory disease; Real-world evidence.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Yes - X.X., J.K., R.K., E.G., and H.S.-F. are or were employees of AstraZeneca at the time of this study and may own stock. J.S. is an employee of Adelphi Real World, which received funding from AstraZeneca to conduct this analysis.
Figures

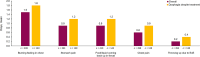


References
-
- Pokrzywinski RM, Harding G, Brooks A, Goodwin B, Williams J. Documenting the journey of patients with eosinophilic esophagitis and the impact of the disease on patients and their caregivers: a cross-sectional, qualitative research study. Adv Ther. 2020;37(10):4458–78. 10.1007/s12325-020-01463-2 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

