Understanding the predictors of health professionals' intention to use electronic health record system: extend and apply UTAUT3 model
- PMID: 39097725
- PMCID: PMC11298108
- DOI: 10.1186/s12913-024-11378-1
Understanding the predictors of health professionals' intention to use electronic health record system: extend and apply UTAUT3 model
Abstract
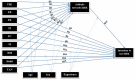
Background: The implementation of Electronic Health Record (EHR) systems is a critical challenge, particularly in low-income countries, where behavioral intention plays a crucial role. To address this issue, we conducted a study to extend and apply the Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology 3 (UTAUT3) model in predicting health professionals' behavioral intention to use EHR systems.
Methods: A quantitative research approach was employed among 423 health professionals in Southwest Ethiopia. We assessed the validity of the proposed model through measurement and structural model statistics. Analysis was done using SPSS AMOS version 23. Hypotheses were tested using structural equation modeling (SEM) analysis, and mediation and moderation effects were evaluated. The associations between exogenous and endogenous variables were examined using standardized regression coefficients (β), 95% confidence intervals, and p-values, with a significance level of p-value < 0.05.
Results: The proposed model outperformed previous UTAUT models, explaining 84.5% (squared multiple correlations (R2) = 0.845) of the variance in behavioral intention to use EHR systems. Personal innovativeness (β = 0.215, p-value < 0.018), performance expectancy (β = 0.245, p-value < 0.001), and attitude (β = 0.611, p-value < 0.001) showed significant associations to use EHR systems. Mediation analysis revealed that performance expectancy, hedonic motivation, and technology anxiety had significant indirect effects on behavioral intention. Furthermore, moderation analysis indicated that gender moderated the association between social influence, personal innovativeness, and behavioral intention.
Conclusion: The extended UTAUT3 model accurately predicts health professionals' intention to use EHR systems and provides a valuable framework for understanding technology acceptance in healthcare. We recommend that digital health implementers and concerned bodies consider the comprehensive range of direct, indirect, and moderating effects. By addressing personal innovativeness, performance expectancy, attitude, hedonic motivation, technology anxiety, and the gender-specific impact of social influence, interventions can effectively enhance behavioral intention toward EHR systems. It is crucial to design gender-specific interventions that address the differences in social influence and personal innovativeness between males and females.
Keywords: Behavioral intention; Electronic health record; Health professionals; Mediation effect; Moderation effect; Structural equation modeling; Technology acceptance; UTAUT; UTAUT2; UTAUT3.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Healthcare providers' acceptance of telemedicine and preference of modalities during COVID-19 pandemics in a low-resource setting: An extended UTAUT model.PLoS One. 2021 Apr 22;16(4):e0250220. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0250220. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33886625 Free PMC article.
-
Analyzing health service employees' intention to use e-health systems in southwest Ethiopia: using UTAUT-2 model.BMC Health Serv Res. 2024 Sep 27;24(1):1136. doi: 10.1186/s12913-024-11567-y. BMC Health Serv Res. 2024. PMID: 39334209 Free PMC article.
-
Intention to use electronic medical record and its predictors among health care providers at referral hospitals, north-West Ethiopia, 2019: using unified theory of acceptance and use technology 2(UTAUT2) model.BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2020 Sep 3;20(1):207. doi: 10.1186/s12911-020-01222-x. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2020. PMID: 32883267 Free PMC article.
-
A scoping review of the drivers and barriers influencing healthcare professionals' behavioral intentions to comply with electronic health record data privacy policy.Health Informatics J. 2024 Oct-Dec;30(4):14604582241296398. doi: 10.1177/14604582241296398. Health Informatics J. 2024. PMID: 39435737
-
Research on elderly users' intentions to accept wearable devices based on the improved UTAUT model.Front Public Health. 2023 Jan 9;10:1035398. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.1035398. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36699866 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The Impact of Leader-Member Relationships on Team Effectiveness Through Speaking Up and Silence: A Cross-Sectional Study in Rural Chinese Hospitals.J Healthc Leadersh. 2024 Dec 12;16:543-555. doi: 10.2147/JHL.S460900. eCollection 2024. J Healthc Leadersh. 2024. PMID: 39691459 Free PMC article.
-
Electronic Nursing Records: Importance for Nursing and Benefits of Implementation in Health Information Systems-A Scoping Review.Nurs Rep. 2024 Nov 18;14(4):3585-3605. doi: 10.3390/nursrep14040262. Nurs Rep. 2024. PMID: 39585153 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Walsham G. Health information systems in developing countries: some reflections on information for action. Inf Technol Dev. 2020;26(1):194–200.10.1080/02681102.2019.1586632 - DOI
-
- Venot A, Burgun A, Quantin C. Medical Informatics, e-Health: Fundamentals and Applications. Cham: Springer International Publishing. 2014;12(3):191–220. 10.1007/978-2-8178-0478-1.
-
- Riazi H, Jafarpour M, Bitaraf E. Towards national ehealth implementation–a comparative study on WHO/ITU national eHealth strategy toolkit in Iran. Studies in Health Technology and Informatics. IOS Press. 2014;205(1):246–50. 10.3233/978-1-61499-432-9-246. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources