DDX19A promotes gastric cancer cell proliferation and migration by activating the PI3K/AKT pathway
- PMID: 39097730
- PMCID: PMC11297674
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-024-03448-5
DDX19A promotes gastric cancer cell proliferation and migration by activating the PI3K/AKT pathway
Abstract
Background: DEAD-box RNA helicase 19 A (DDX19A) is overexpressed in cervical squamous cell carcinoma. However, its role in gastric cancer remains unclear. The present study aimed to explore the role and underlying mechanism of DDX19A in the development of gastric cancer.
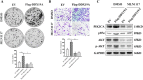
Methods: The expression of DDX19A in gastric cancer and paracancerous tissues was evaluated through quantitative polymerase chain reaction, western blotting, and immunohistochemical staining. The biological functions of DDX19A in gastric cancer were determined using CCK8, plate colony-forming, and Transwell migration assays. The specific mechanism of DDX19A in gastric cancer cells was studied using western blotting, RNA-binding protein immunoprecipitation, mRNA half-life detection, and nuclear and cytoplasmic RNA isolation.
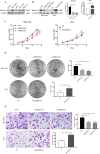
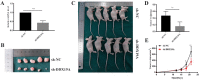
Results: DDX19A was highly expressed in gastric cancer and positively associated with malignant clinicopathological features and poor prognosis. Additionally, DDX19A promoted gastric cancer cell proliferation, migration, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition phenotypes. Mechanistically, DDX19A activated the PI3K/AKT pathway by upregulating phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PIK3CA) expression. Furthermore, DDX19A interacted with PIK3CA mRNA, stabilized it, and facilitated its export from the nucleus.
Conclusions: Our study reveals a novel mechanism whereby DDX19A promotes the proliferation and migration of gastric cancer cells by enhancing the stability and nuclear export of PIK3CA mRNA, thereby activating the PI3K/AKT pathway.
Keywords: DDX19A; Gastric cancer; Nuclear export; PI3K/AKT; PIK3CA.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
Grants and funding
- BJK2023001/the Science and Technology Project of Hebei Education Department
- BJK2023001/the Science and Technology Project of Hebei Education Department
- H2022406025/the Natural Science Fund of Hebei
- No. 202201/the High-level Talents Research Startup Fund of Chengde Medical College
- No. 202201/the High-level Talents Research Startup Fund of Chengde Medical College
- No. 202201/the High-level Talents Research Startup Fund of Chengde Medical College
- No. 202201/the High-level Talents Research Startup Fund of Chengde Medical College
- H2020406008, 236Z7701G/the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province, China
- H2020406008, 236Z7701G/the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province, China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

