Honokiol relieves hippocampal neuronal damage in Alzheimer's disease by activating the SIRT3-mediated mitochondrial autophagy
- PMID: 39097923
- PMCID: PMC11298204
- DOI: 10.1111/cns.14878
Honokiol relieves hippocampal neuronal damage in Alzheimer's disease by activating the SIRT3-mediated mitochondrial autophagy
Abstract
Background: This work elucidated the effect of honokiol (HKL) on hippocampal neuronal mitochondrial function in Alzheimer's disease (AD).
Methods: APP/PS1 mice were used as AD mice models and exposed to HKL and 3-TYP. Morris water maze experiment was performed to appraise cognitive performance of mice. Hippocampal Aβ+ plaque deposition and neuronal survival was evaluated by immunohistochemistry and Nissl staining. Hippocampal neurons were dissociated from C57BL/6 mouse embryos. Hippocampal neuronal AD model was constructed by Aβ oligomers induction and treated with HKL, CsA and 3-TYP. Neuronal viability and apoptosis were detected by cell counting kit-8 assay and TUNEL staining. mRFP-eGFP-LC3 assay, MitoSOX Red, dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate, and JC-1 staining were performed to monitor neuronal autophagosomes, mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS), neuronal ROS, and mitochondrial membrane potential. Autophagy-related proteins were detected by Western blot.
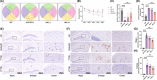
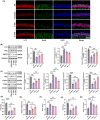
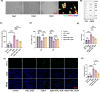
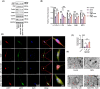
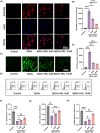
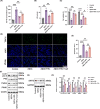
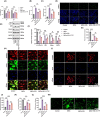
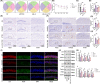
Results: In AD mice, HKL improved cognitive function, relieved hippocampal Aβ1-42 plaque deposition, promoted hippocampal neuron survival, and activated hippocampal SIRT3 expression and mitochondrial autophagy. These effects of HKL on AD mice were abolished by 3-TYP treatment. In hippocampal neuronal AD model, HKL increased neuronal activity, attenuated neuronal apoptosis and Aβ aggregation, activated SIRT3 and mitochondrial autophagy, reduced mitochondrial and neuronal ROS, and elevated mitochondrial membrane potential. CsA treatment and 3-TYP treatment abrogated the protection of HKL on hippocampal neuronal AD model. The promotion of mitochondrial autophagy by HKL in hippocampal neuronal AD model was counteracted by 3-TYP.
Conclusions: HKL activates SIRT3-mediated mitochondrial autophagy to mitigate hippocampal neuronal damage in AD. HKL may be effective in treating AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; SIRT3; honokiol; mitochondrial autophagy; neuronal damage.
© 2024 The Author(s). CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to report.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The effects of Honokiol on the liver of Alzheimer's disease mice by upregulating SIRT3.J Alzheimers Dis. 2025 Aug 8:13872877251362185. doi: 10.1177/13872877251362185. Online ahead of print. J Alzheimers Dis. 2025. PMID: 40776632
-
Honokiol improves cognitive impairment in APP/PS1 mice through activating mitophagy and mitochondrial unfolded protein response.Chem Biol Interact. 2022 Jan 5;351:109741. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2021.109741. Epub 2021 Nov 6. Chem Biol Interact. 2022. PMID: 34752757
-
Honokiol Attenuates Oligomeric Amyloid β1-42-Induced Alzheimer's Disease in Mice Through Attenuating Mitochondrial Apoptosis and Inhibiting the Nuclear Factor Kappa-B Signaling Pathway.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;43(1):69-81. doi: 10.1159/000480320. Epub 2017 Aug 25. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28848085
-
Honokiol Targeting SIRT3: From Molecular Mechanisms to Therapeutic Opportunities.FASEB J. 2025 Jul 15;39(13):e70798. doi: 10.1096/fj.202501428R. FASEB J. 2025. PMID: 40590114 Review.
-
Mitochondrial Damage and Autophagy Dysregulation in Alzheimer's Disease: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Opportunities.Neurochem Res. 2025 Jul 28;50(4):251. doi: 10.1007/s11064-025-04490-z. Neurochem Res. 2025. PMID: 40719892 Review.
Cited by
-
Irisin Regulates Microglia M1/M2 Polarization and Promotes Autophagy Through the Sirt3 Pathway to Alleviate POCD.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2025 Apr 11;20(1):34. doi: 10.1007/s11481-025-10201-w. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40214830
-
Sirtuin-3 activation by honokiol attenuated anesthesia/surgery-induced cognitive impairment and neuronal ferroptosis via inhibiting mitochondrial GPX4 acetylation.J Nanobiotechnology. 2025 Jun 4;23(1):414. doi: 10.1186/s12951-025-03502-y. J Nanobiotechnology. 2025. PMID: 40462120 Free PMC article.
-
Honokiol induces paraptosis-like cell death through mitochondrial ROS-dependent endoplasmic reticulum stress in hepatocellular carcinoma Hep3B cells.Toxicol Res. 2025 Apr 6;41(4):385-396. doi: 10.1007/s43188-025-00291-2. eCollection 2025 Jul. Toxicol Res. 2025. PMID: 40612520
-
Aloe-Emodin Improves Mitophagy in Alzheimer's Disease via Activating the AMPK/PGC-1α/SIRT3 Signaling Pathway.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2025 Mar;31(3):e70346. doi: 10.1111/cns.70346. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2025. PMID: 40125832 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Faulin T, Estadella D. Alzheimer's disease and its relationship with the microbiota‐gut‐brain axis. Arq Gastroenterol. 2023;60(1):144‐154. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

