The interplay between doxorubicin chemotherapy, antioxidant system, and cardiotoxicity: Unrevealing of the protective potential of tannic acid
- PMID: 39099314
- PMCID: PMC11798539
- DOI: 10.1002/bab.2648
The interplay between doxorubicin chemotherapy, antioxidant system, and cardiotoxicity: Unrevealing of the protective potential of tannic acid
Abstract
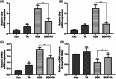
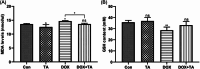
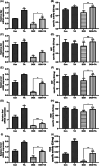
Cardiotoxicity is the leading side effect of anthracycline-based chemotherapy. Therefore, it has gained importance to reveal chemotherapy-supporting strategies and reliable agents with their mechanisms of action. Tannic acid (TA), a naturally occurring plant polyphenol, has diverse physiological effects, including anti-inflammatory, anticarcinogenic, antioxidant, and radical scavenging properties. Therefore, this study was designed to investigate whether TA exerts a protective effect on mechanisms contributing to anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity in rat heart tissues exposed to doxorubicin (DOX). Rats were randomly divided into control and experimental groups and treated with (18 mg/kg) DOX, TA (50 mg/kg), and DOX + TA during the 2 weeks. Cardiac gene markers and mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) content were evaluated in the heart tissues of all animals. In addition to major metabolites, mRNA expression changes and biological activity responses of components of antioxidant metabolism were examined in the heart tissues of all animals. The expression of cardiac gene markers increased by DOX exposure was significantly reduced by TA treatment, whereas mtDNA content, which was decreased by DOX exposure, was significantly increased. TA also improved antioxidant metabolism members' gene expression and enzymatic activity, including glutathione peroxidase, glutathione s-transferase, superoxide dismutase, catalase, and thioredoxin reductase. This study provides a detailed overview of the current understanding of DOX-induced cardiotoxicity and preventive or curative measures involving TA.
Keywords: antioxidant system; cardiotoxicity; doxorubicin; heart; tannic acid.
© 2024 The Author(s). Biotechnology and Applied Biochemistry published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Protective effects of tannic acid on acute doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity: Involvement of suppression in oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis.Biomed Pharmacother. 2017 Sep;93:1253-1260. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.07.051. Epub 2017 Jul 20. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017. PMID: 28738542
-
Irvingia gabonensis Seed Extract: An Effective Attenuator of Doxorubicin-Mediated Cardiotoxicity in Wistar Rats.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020 Oct 22;2020:1602816. doi: 10.1155/2020/1602816. eCollection 2020. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020. PMID: 33149803 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of the multi-targeted protection potential of tannic acid against doxorubicin-induced kidney damage in rats.Chem Biol Interact. 2022 Sep 25;365:110111. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2022.110111. Epub 2022 Aug 18. Chem Biol Interact. 2022. PMID: 35987278
-
The hepatoprotective potential of tannic acid against doxorubicin-induced hepatotoxicity: Insights into its antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, and antiapoptotic mechanisms.J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2024 Aug;38(8):e23798. doi: 10.1002/jbt.23798. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 39108104
-
The role of hesperidin as a cardioprotective strategy against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity: The antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antiapoptotic, and cytoprotective potentials.Open Vet J. 2023 Dec;13(12):1718-1728. doi: 10.5455/OVJ.2023.v13.i12.20. Epub 2023 Dec 31. Open Vet J. 2023. PMID: 38292716 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Identification of dilated cardiomyopathy-linked key genes by bioinformatics methods and evaluating the impact of tannic acid and monosodium glutamate in rats.Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 2025 Apr;72(2):377-387. doi: 10.1002/bab.2670. Epub 2024 Sep 25. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 2025. PMID: 39318238 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of the effects of monosodium glutamate and tannic acid on the glutathione and thioredoxin systems in the liver of rats.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 May 21. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-04279-5. Online ahead of print. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40397121
References
-
- Öztürk N, Karağaç MS, Yeşilkent EN, Isıyel M, Tosun H, Karadaş H, et al. Exploring Esculetin's protective role: countering doxorubicin‐induced oxidative stress in rat heart. J Lab Anim Sci Pract. 2024;4(1):44–52. 10.5281/zenodo.10892230 - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

