Prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension in community-dwelling older adults with chronic kidney disease: the Irish longitudinal study on ageing
- PMID: 39099566
- PMCID: PMC11292221
- DOI: 10.1093/ckj/sfae184
Prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension in community-dwelling older adults with chronic kidney disease: the Irish longitudinal study on ageing
Abstract
Background: Hypertension is highly prevalent in chronic kidney disease (CKD), posing a significant but modifiable risk for adverse clinical outcomes. This study explored the prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension in older Irish adults with CKD.
Methods: Data were analysed from participants in Wave 1 of The Irish Longitudinal Study on Ageing (TILDA) who were aged 50 years and older. CKD was defined as eGFR <60 ml/min/1.72 m2, hypertension defined as systolic blood pressure (SBP) ≥140 mmHg and/or diastolic blood pressure (DBP) ≥90 mmHg and/or self-reported use of antihypertensive medication. Participant awareness and treatment of hypertension was based on self-report and SBP/DBP <140/90 mmHg. Multivariable logistic regression examined relationships with awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension expressed as adjusted odds ratios.
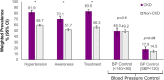
Results: Prevalence of hypertension was significantly higher in participants with CKD than without (81.9% vs 59.7%, P < .001). Among hypertensive individuals, 70.1% (95% CI: 65.8-74.1) were aware, 83.5% (95% CI 80.0-86.6) were on treatment, yet blood pressure control <140/90 mmHg and SBP <120 mmHg were achieved in only 49.3% (CI 44.0-54.7%) and 17.9% (CI 14.4-22.1), respectively. In multivariable analysis, advancing age 1.05 (CI 1.01-1.10), obesity 6.23 (CI 2.51-15.5), diabetes 5.78 (CI 1.55-21.5), and cardiovascular disease 9.89 (CI 3.27-29.9) were associated with higher odds of treatment, while cardiovascular disease 2.35 (CI 1.39-3.99) and combination antihypertensive therapy 1.76 (CI 1.03-3.01) were associated with blood pressure control.
Conclusion: The prevalence of hypertension is substantial in older Irish adults with CKD; however, control is poor. Approximately, one-third of participants were unaware of their hypertensive status and approximately one-fifth were untreated.
Keywords: CKD; blood pressure; epidemiology; guidelines; hypertension.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the ERA.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Foreman KJ, Marquez N, Dolgert A et al. Forecasting life expectancy, years of life lost, and all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 250 causes of death: reference and alternative scenarios for 2016–40 for 195 countries and territories. Lancet North Am Ed 2018;392:2052–90. 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31694-5 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

