Evaluation of destruction of bacterial membrane structure associated with anti-quorum sensing and ant-diabetic activity of Cyperus esculentus extract
- PMID: 39100488
- PMCID: PMC11295847
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34128
Evaluation of destruction of bacterial membrane structure associated with anti-quorum sensing and ant-diabetic activity of Cyperus esculentus extract
Abstract
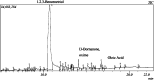
Recently, there has been an increasing demand for medicinal plants to control diseases for good health and well-being, as primary health facilities are inadequate in certain populations to cure infections. Since synthetic medicines are toxic to humans and other animals, the present research is thus focused on using traditional medicine for treating various ailments as they are harmless. Based on the above facts, the current study was conducted to assay the antimicrobial, anti-diabetic, anti-cholinesterase, anti-oxidant, anti-quorum sensing, and anti-antibiotic resistance modifying effect of extracts of Cyperus esculentus. This study found 37 and 30 chemicals in butanol and dichloromethane (DCM) extracts using a gas chromatograph mass spectrophotometer (GC-MS). Most active compounds identified were benzofuran, 2,3-dihydro-, 1,2,3-benzenetriol, 3-bornanone, oxime and oleic acid by extracts of butanol whereas dichloromethane extracted three major active compounds (2,3-dihydro-3,5-dihydroxy-, 4H-pyran-4-one 3-deoxy-d-mannoic lactone and 5-hydroxymethylfurfural). Both dichloromethane and butanol extracts showed the highest antimicrobial activity. Compared to aqueous extracts, dichloromethane, and butanol showed excellent anti-diabetic anti-cholinesterase activities and inhibited virulence factors regulated by quorum sensing (QS). Anti-oxidants increased in solvent extracts (DCM and butanol) compared to aqueous extracts. Results of scanning electron microscope (SEM) and Fourier Transmission Infrared (FTIR) indicated damage to the cell membrane of S. aureus by the formation of pits and breakage in functional groups exposed to the extracts of butanol and dichloromethane compared to aqueous extracts. The above results confirmed that C. esculentus can be an alternative medicine for treating diseases.
Keywords: Anti-diabetic effect; Antibacterial activity; Antifungal activity; Cell damage; Cell-to-cell communication; Cyperus esculentus; Secondary metabolites.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Antimicrobial and anti-Quorum Sensing activities of selected medicinal plants of Ethiopia: Implication for development of potent antimicrobial agents.BMC Microbiol. 2016 Jul 11;16(1):139. doi: 10.1186/s12866-016-0765-9. BMC Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27400878 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the anti-virulence potential of plants used in traditional Mayan medicine to treat bacterial infections.J Ethnopharmacol. 2023 Dec 5;317:116783. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.116783. Epub 2023 Jun 14. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37321428
-
Attenuation of quorum sensing regulated virulence functions and biofilm of pathogenic bacteria by medicinal plant Artemisia annua and its phytoconstituent 1, 8-cineole.Microsc Res Tech. 2024 Jan;87(1):133-148. doi: 10.1002/jemt.24418. Epub 2023 Sep 20. Microsc Res Tech. 2024. PMID: 37728140
-
Cyperus (Cyperus esculentus L.): A Review of Its Compositions, Medical Efficacy, Antibacterial Activity and Allelopathic Potentials.Plants (Basel). 2022 Apr 21;11(9):1127. doi: 10.3390/plants11091127. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35567128 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-Quorum Sensing Natural Compounds.J Microsc Ultrastruct. 2018 Jan-Mar;6(1):1-10. doi: 10.4103/JMAU.JMAU_10_18. J Microsc Ultrastruct. 2018. PMID: 30023261 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting Agrobacterium tumefaciens: A Computational Study on Quorum Sensing Inhibition.J Basic Microbiol. 2025 Jul;65(7):e70041. doi: 10.1002/jobm.70041. Epub 2025 Apr 22. J Basic Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40264335 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shanmugam S., Bhavani P. Studies on the comparison of phytochemical constituents and antimicrobial activity of Curcuma longa varieties. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2014;3:573–581.
-
- Haouam C., Boudiba S., Tamfu A.N., Kucukaydin S., Hanini K., Zohra H.F., Hioun S., Botezatu A.D., Ceylan Ö., Boudiba L., et al. Assessment of chemical composition and in vitro anti-oxidant, anti-diabetic, anti-cholinesterase, and microbial virulence-quenching effects of Salad burnet (Sanguisorba minor L.) Harvested from Algeria. Plants. 2023;12:4134. doi: 10.3390/plants12244134. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Adelaja B.A., Adebayo O.S., Adejoro M.A., Nwanguma E.I. Innovative food trends: species. Food Technol. 2008;43:102–106.
-
- Mehtab P., Ali M.M., Mahbbob A., Faheem A., Pedro S.P.S., Manuela R.S. Two new phenolic compounds from Ficus rumphii and their antiproliferative activity. J. Nat. Prod. Res. 2014;28:646–652. - PubMed
-
- Kaur R., Kapoor K., Kaur H. Plants as a source of anticancer agents. J. Nat. Prod. Plant Resour. 2011;1:119–124.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

