Effectiveness of Vortioxetine for the Treatment of Emotional Blunting in Patients with Major Depressive Disorder Experiencing Inadequate Response to SSRI/SNRI Monotherapy in Spain: Results from the COMPLETE Study
- PMID: 39100571
- PMCID: PMC11297586
- DOI: 10.2147/NDT.S473056
Effectiveness of Vortioxetine for the Treatment of Emotional Blunting in Patients with Major Depressive Disorder Experiencing Inadequate Response to SSRI/SNRI Monotherapy in Spain: Results from the COMPLETE Study
Abstract
Background: The multinational, open-label COMPLETE study (NCT03835715) investigated the effectiveness of vortioxetine in alleviating emotional blunting in patients with major depressive disorder (MDD) experiencing inadequate response and emotional blunting while being treated with a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) or serotonin-noradrenaline reuptake inhibitor (SNRI). This paper presents results for the subgroup of patients enrolled in Spain.
Methods: Patients with MDD (n = 67) experiencing partial response and emotional blunting during monotherapy with an SSRI or SNRI were switched to vortioxetine (10-20 mg/day) for 8 weeks. The primary study outcome was emotional blunting, assessed by the Oxford Depression Questionnaire (ODQ).
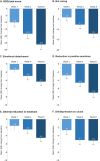
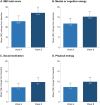
Results: After 8 weeks of vortioxetine, the mean (SE) change in ODQ total score from baseline was -26.0 (2.9) (P < 0.001). Respective changes in Montgomery-Åsberg Depression Rating Scale (MADRS), Motivation and Energy Inventory, Digit Symbol Substitution Test, and Sheehan Disability Scale (SDS) total scores were -14.9 (0.8), +34.2 (4.5), +6.3 (1.6), and ‒9.0 (1.3) (all P < 0.001 vs baseline). At week 8, 70.4% of patients no longer reported emotional blunting and 53.7% had achieved remission from their depressive symptoms (defined as a MADRS total score ≤10). Mediation analysis showed 77.1% of the change in SDS total score to be a direct effect of the improvement in ODQ total score after switching to vortioxetine. Adverse events were reported by 35 patients (52.2%), most commonly nausea (14 patients, 20.9%). At week 8, 33/54 patients (61.1%) were receiving vortioxetine 20 mg/day.
Conclusion: In this study investigating the effectiveness of vortioxetine in Spanish patients with MDD who experienced inadequate response and emotional blunting on SSRI/SNRI monotherapy, significant improvements in emotional blunting, core depressive symptoms (including anhedonia), sleep duration, motivation and energy, cognitive performance, and overall patient functioning were observed during the 8 weeks of treatment. Two-thirds of patients no longer reported emotional blunting and over half were in remission from their depressive symptoms at week 8.
Keywords: emotional blunting; energy; major depressive disorder; motivation; patient functioning; vortioxetine.
© 2024 Christensen et al.
Conflict of interest statement
MCC and HL are employees of H. Lundbeck A/S. FC has received consultancy fees or honoraria/research grants in the last 5 years from Exeltis, IdISBa, Janssen Cilag, Lundbeck, Otsuka, Pfizer Angelini, Servier. ALM has received consultancy fees or honoraria/research grants in the last 5 years from Boehringer Ingelheim, Casen Recordati, Eli Lilly, Forum Pharmaceuticals, Instituto de Salud Carlos III, Janssen Cilag, Lundbeck, Otsuka, Pfizer, Roche, ROVI, Servier, and the Junta de Castilla y León. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effectiveness of Vortioxetine on Emotional Blunting in Patients with Major Depressive Disorder with inadequate response to SSRI/SNRI treatment.J Affect Disord. 2021 Mar 15;283:472-479. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2020.11.106. Epub 2020 Nov 19. J Affect Disord. 2021. PMID: 33516560
-
Validation of the Oxford Depression Questionnaire: Sensitivity to change, minimal clinically important difference, and response threshold for the assessment of emotional blunting.J Affect Disord. 2021 Nov 1;294:924-931. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2021.07.099. Epub 2021 Jul 31. J Affect Disord. 2021. PMID: 34378539
-
A randomised, double-blind study in adults with major depressive disorder with an inadequate response to a single course of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor or serotonin-noradrenaline reuptake inhibitor treatment switched to vortioxetine or agomelatine.Hum Psychopharmacol. 2014 Sep;29(5):470-82. doi: 10.1002/hup.2424. Hum Psychopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25087600 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A meta-analysis of randomized, placebo-controlled trials of vortioxetine for the treatment of major depressive disorder in adults.Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2016 Jun;26(6):979-93. doi: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2016.03.007. Epub 2016 Mar 25. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27139079 Review.
-
[Vortioxetine: a new antidepressant to treat depressive episodes].Encephale. 2016 Feb;42(1):48-58. doi: 10.1016/j.encep.2015.07.007. Epub 2015 Sep 8. Encephale. 2016. PMID: 26358483 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Optimizing the diagnosis and treatment of depression in primary care: the emerging role of vortioxetine treatment.Front Psychiatry. 2025 Jul 1;16:1568777. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2025.1568777. eCollection 2025. Front Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 40666435 Free PMC article.
-
Anhedonia as a Core Symptom of Depression and a Construct for Biological Research.Focus (Am Psychiatr Publ). 2025 Apr;23(2):163-172. doi: 10.1176/appi.focus.20240050. Epub 2025 Apr 15. Focus (Am Psychiatr Publ). 2025. PMID: 40235618
References
-
- World Health Organization. Depression and Other Common Mental Disorders: Global Health Estimates. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2017. Available from: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/254610/WHO-MSD-MER-2017.... Accessed February 22, 2023.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

