COVID-19 Vaccines Breakthrough Infections and Adverse Effects Reported by the Birzeit University Community in Palestine
- PMID: 39100722
- PMCID: PMC11297544
- DOI: 10.2147/IJGM.S466838
COVID-19 Vaccines Breakthrough Infections and Adverse Effects Reported by the Birzeit University Community in Palestine
Abstract
Background: Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) vaccines play an essential role in boosting immunity, preventing severe diseases, and alleviating the Covid-19 health crisis.
Objective: This study aimed to explore the type and severity of short-term adverse reactions associated with BNT162 (Pfizer-BioNTech), mRNA 1273 (Moderna), and viral vector vaccines and to compare the incidence of post-vaccination Covid-19 infection among the Birzeit University community in Palestine.
Methods: This questionnaire-based retrospective cross-sectional study was conducted among individuals who were vaccinated with at least one dose of any COVID-19 vaccine offered in Palestine during the COVID-19 pandemic. The study included participants aged 18 years and older who were vaccinated with Pfizer, Moderna, Sputnik Light, or Sputnik v.
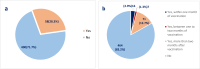
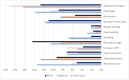
Results: A total of 558 participants who were administered COVID-19 vaccine were included in the study. Sputnik (239), Pfizer vaccine recipients (236), and Moderna vaccine recipients (83). Of the viral vector vaccine recipients, 57 (23.8%) had a post-vaccination infection, compared to 30 (12.7%) for Pfizer and seven (8.4%) for Moderna. Furthermore, the reported adverse effects in the viral victor group were higher than those in the Moderna and Pfizer groups (71.7, 66.3, and 61.9%, respectively). Chills, headache, fatigue, abdominal pain, and joint pain were significantly higher in the Viral Vector vaccine group than the Moderna and Pfizer vaccine. Vomiting, tiredness, and fatigue were significantly less likely to be complained of by Pfizer vaccine recipients compared to Moderna and Viral Vector vaccine recipients (p < 0.05).
Conclusions: Breakthrough infections were associated with both viral vectors and mRNA; however, the mRNA vaccine had less reported post-vaccine infection. Furthermore, the Pfizer/BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine group reported fewer commonly reported side effects (fever, chills, headache, fatigue, muscle pain, joint pain, nausea, and dizziness), followed by the Moderna and viral vector vaccines. Females and underweight participants experienced more adverse effects with both vaccines, and fewer common side effects were reported by all participants.
Keywords: Covid-19 vaccine; Moderna; Palestine; Pfizer; Sputnik; adverse effects; breakthrough infection; viral vector vaccine.
© 2024 Abukhalil et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures



References
-
- World Health Organization. WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19 Dashboard); Available from: https://data.who.int/dashboards/covid19/cases?n=c. Accessed May 4, 2024.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

