Early Childhood Screen Use Contexts and Cognitive and Psychosocial Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
- PMID: 39102255
- PMCID: PMC12527480
- DOI: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2024.2620
Early Childhood Screen Use Contexts and Cognitive and Psychosocial Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Abstract
Importance: The multifaceted nature of screen use has been largely overlooked in favor of a simplistic unidimensional measure of overall screen time when evaluating the benefits and risks of screen use to early childhood development.
Objective: To conduct a systematic review and meta-analysis to examine associations of screen use contexts in early childhood with cognitive and psychosocial outcomes.
Data sources: PsycINFO, Embase, MEDLINE Ovid, ProQuest, CINAHL, Web of Science, and Scopus were searched from inception to December 31, 2023.
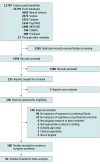
Study selection: A total of 7441 studies were initially identified. Studies were included if they examined associations between a contextual factor of screen use among children aged 0 to 5.99 years and cognitive or psychosocial development. Observational, experimental, and randomized clinical trial study designs were included.
Data extraction and synthesis: All studies were independently screened in duplicate following PRISMA guidelines. Effect sizes of associations (r) from observational studies were pooled using random-effects 3-level meta-analyses. The remaining study designs were narratively synthesized.
Main outcomes and measures: Screen use contexts included content (child directed and age inappropriate), type (program viewing and game or app use), co-use (or solo use), background television, caregiver screen use during child routines, and purpose. Outcomes were cognitive (executive functioning, language, and academic skills) or psychosocial (internalizing and externalizing behavior problems and socioemotional competence).
Results: Overall, 100 studies (176 742 participants) were included, and of these, 64 observational studies (pooled sample sizes ranging from 711 to 69 232) were included in meta-analyses. Program viewing (n = 14; k = 48; r, -0.16; 95% CI, -0.24 to -0.08) and background television (n = 8; k = 18; r, -0.10; 95% CI, -0.18 to -0.02) were negatively associated with cognitive outcomes, while program viewing (n = 6; k = 31; r, -0.04; 95% CI, -0.07 to -0.01), age-inappropriate content (n = 9; k = 36; r, -0.11; 95% CI, -0.17 to -0.04), and caregiver screen use during routines (n = 6; k = 14; r, -0.11; 95% CI, -0.20 to -0.03) were negatively associated with psychosocial outcomes. Co-use was positively associated with cognitive outcomes (n = 8; k = 28; r, 0.14; 95% CI, 0.03 to 0.25).
Conclusions and relevance: Findings show small to moderate effect sizes that highlight the need to consider screen use contexts when making recommendations for families, clinicians, and educators beyond screen time limits; including encouraging intentional and productive screen use, age-appropriate content, and co-use with caregivers.
Conflict of interest statement
References
-
- Rideout V, Robb MB. The common sense census: media use by kids age zero to eight, 2020. Common Sense Media . Accessed December 6, 2023. https://www.commonsensemedia.org/sites/default/files/research/report/202...
-
- Wartella E, Rideout V, Lauricella AR, Connell S. Parenting in the age of digital technology. Northwestern University’s Center on Media and Human Development . 2013. Accessed December 6, 2023. https://sites.utexas.edu/contemporaryfamilies/files/2014/04/Wartella.pdf
-
- The Royal Children’s Hospital National Child Health Poll . Top ten child health problems: what the public thinks. 2021. Accessed November 24, 2023. https://rchpoll.org.au/polls/top-10-child-health-problems/
-
- Straker L, Edwards S, Kervin L, Burley J, Hendry D, Cliff D. Moving screen use guidelines: Nine reasons why screen use guidelines should be separated from public health 24-hour movement guidelines in Australia and internationally. ARC Centre of Excellence for the Digital Child . 2023. Accessed January 15, 2024. https://digitalchild.org.au/research/publications/working-paper/moving-s...
-
- World Health Organization . Guidelines on Physical Activity, Sedentary Behaviour and Sleep for Children Under 5 Years of Age. World Health Organization; 2019. - PubMed