Outcomes With Postrecurrence Systemic Therapy Following Adjuvant Checkpoint Inhibitor Treatment for Resected Melanoma in CheckMate 238
- PMID: 39102624
- PMCID: PMC11527380
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.23.01448
Outcomes With Postrecurrence Systemic Therapy Following Adjuvant Checkpoint Inhibitor Treatment for Resected Melanoma in CheckMate 238
Abstract
Purpose: In phase III CheckMate 238, adjuvant nivolumab significantly improved recurrence-free survival compared with ipilimumab in patients with resected stage IIIB-C/IV melanoma without a significant difference in overall survival (OS). Here, we investigate progression-free survival (PFS) and OS after postrecurrence systemic therapy.
Patients and methods: Patients 15 years or older with resected stage IIIB-C/IV melanoma were stratified by stage and tumor PD-L1 status and randomly assigned to receive nivolumab 3 mg/kg every 2 weeks, or ipilimumab 10 mg/kg every 3 weeks for four doses and then every 12 weeks for 1 year or until disease recurrence, unacceptable toxicity, or withdrawal of consent. Patients with recurrence in each group were assessed for PFS and OS from subsequent systemic therapy (SST) initiation per recurrence timing (≤12 months [early] v >12 months [late] from initial therapy).
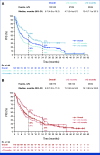
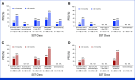
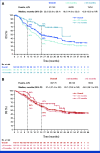
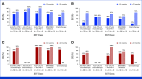
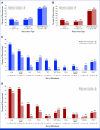
Results: Recurrences occurred in 198 (44%) of 453 nivolumab-treated patients (122 early, 76 late) and 232 (51%) of 453 ipilimumab-treated patients (160 early, 72 late). Median PFS on next-line systemic therapy for nivolumab-treated patients recurring early versus late was 4.7 versus 12.4 months (24-month rates, 16% v 31%); median OS was 19.8 versus 42.8 months (24-month rates: 37% v 73%). In response to subsequent therapy, patients on nivolumab with late versus early recurrence were more likely to benefit from anti-PD-1 monotherapy. Nivolumab-treated patients with either an early or late recurrence benefitted from an ipilimumab-based therapy or targeted therapy, each with similar OS.
Conclusion: Postrecurrence survival was longer for patients who recurred >12 months. Patients on nivolumab who recurred early benefitted from SST but had better survival with ipilimumab-based regimens or targeted therapy compared with anti-PD-1 monotherapy.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02388906.
Conflict of interest statement
The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated unless otherwise noted. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. For more information about ASCO's conflict of interest policy, please refer to
Open Payments is a public database containing information reported by companies about payments made to US-licensed physicians (
Figures
Comment in
-
How to treat systemic recurrences following adjuvant immunotherapy.Transl Cancer Res. 2025 Jun 30;14(6):3277-3280. doi: 10.21037/tcr-2025-505. Epub 2025 Jun 23. Transl Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40687250 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Eggermont AM, Chiarion-Sileni V, Grob JJ, et al. Adjuvant ipilimumab versus placebo after complete resection of high-risk stage III melanoma (EORTC 18071): A randomised, double-blind, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16:522–530. - PubMed
-
- Long GV, Hauschild A, Santinami M, et al. Adjuvant dabrafenib plus trametinib in stage III BRAF-mutated melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2017;377:1813–1823. - PubMed
-
- Weber J, Mandala M, Del Vecchio M, et al. Adjuvant nivolumab versus ipilimumab in resected stage III or IV melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2017;377:1824–1835. - PubMed
-
- Eggermont AMM, Blank CU, Mandala M, et al. Adjuvant pembrolizumab versus placebo in resected stage III melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2018;378:1789–1801. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

