Trastuzumab Deruxtecan in Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2-Expressing Biliary Tract Cancer (HERB; NCCH1805): A Multicenter, Single-Arm, Phase II Trial
- PMID: 39102634
- PMCID: PMC11404765
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.23.02010
Trastuzumab Deruxtecan in Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2-Expressing Biliary Tract Cancer (HERB; NCCH1805): A Multicenter, Single-Arm, Phase II Trial
Abstract
Purpose: Treatment options for patients with unresectable or recurrent biliary tract cancer (BTC) who progress on a gemcitabine-containing regimen are limited. In addition, the significance of anti-human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) therapy in HER2-expressing BTC has not been sufficiently investigated.
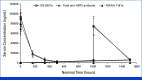
Methods: In this phase II trial, participants from five institutions in Japan were enrolled. Eligible patients had pathologically confirmed unresectable or recurrent BTC with centrally confirmed HER2-positive (immunohistochemistry [IHC]3+ or IHC2+ and in situ hybridization [ISH]+) or HER2-low (IHC2+ and ISH-, IHC1+, and IHC0 and ISH+) and were refractory or intolerant to a gemcitabine-containing regimen. The patients received 5.4 mg/kg trastuzumab deruxtecan (T-DXd) once every 3 weeks until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. The primary end point was the confirmed objective response rate (ORR) in HER2-positive BTC by an independent central review (threshold ORR, 15%; expected ORR, 40%).
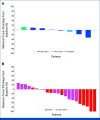
Results: A total of 32 patients were enrolled and treated. Among these patients, 22 with HER2-positive disease comprised the primary efficacy population and had a confirmed ORR of 36.4% (90% CI, 19.6 to 56.1; P = .01), meeting the primary end point. Eight with HER2-low disease comprised the exploratory population and had a confirmed ORR of 12.5%. The most common ≥grade 3 treatment-related adverse events were anemia (53.1%) and neutropenia (31.3%). Eight patients (25.0%) had interstitial lung disease (ILD), including two grade 5 events.
Conclusion: T-DXd showed promising activity in patients with HER2-positive BTC and a signal of efficacy in patients with HER2-low BTC. Although the safety profile was generally manageable, ILD requires careful monitoring and early intervention.
Conflict of interest statement
The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated unless otherwise noted. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. For more information about ASCO's conflict of interest policy, please refer to
Open Payments is a public database containing information reported by companies about payments made to US-licensed physicians (
Figures



References
-
- Valle JW, Kelley RK, Nervi B, et al. : Biliary tract cancer. Lancet 397:428-444, 2021 - PubMed
-
- Banales JM, Cardinale V, Carpino G, et al. : Expert consensus document: Cholangiocarcinoma: Current knowledge and future perspectives consensus statement from the European Network for the Study of Cholangiocarcinoma (ENS-CCA). Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 13:261-280, 2016 - PubMed
-
- Valle J, Wasan H, Palmer DH, et al. : Cisplatin plus gemcitabine versus gemcitabine for biliary tract cancer. N Engl J Med 362:1273-1281, 2010 - PubMed
-
- Oh D-Y, Ruth He A, Qin S, et al. : Durvalumab plus gemcitabine and cisplatin in advanced biliary tract cancer. NEJM Évid 1:EVIDoa2200015, 2022 - PubMed
-
- Kelley RK, Ueno M, Yoo C, et al. : Pembrolizumab in combination with gemcitabine and cisplatin compared with gemcitabine and cisplatin alone for patients with advanced biliary tract cancer (KEYNOTE-966): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 401:1853-1865, 2023 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

