A neurodevelopmental disorder mutation locks G proteins in the transitory pre-activated state
- PMID: 39103320
- PMCID: PMC11300612
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-50964-z
A neurodevelopmental disorder mutation locks G proteins in the transitory pre-activated state
Abstract
Many neurotransmitter receptors activate G proteins through exchange of GDP for GTP. The intermediate nucleotide-free state has eluded characterization, due largely to its inherent instability. Here we characterize a G protein variant associated with a rare neurological disorder in humans. GαoK46E has a charge reversal that clashes with the phosphate groups of GDP and GTP. As anticipated, the purified protein binds poorly to guanine nucleotides yet retains wild-type affinity for G protein βγ subunits. In cells with physiological concentrations of nucleotide, GαoK46E forms a stable complex with receptors and Gβγ, impeding effector activation. Further, we demonstrate that the mutant can be easily purified in complex with dopamine-bound D2 receptors, and use cryo-electron microscopy to determine the structure, including both domains of Gαo, without nucleotide or stabilizing nanobodies. These findings reveal the molecular basis for the first committed step of G protein activation, establish a mechanistic basis for a neurological disorder, provide a simplified strategy to determine receptor-G protein structures, and a method to detect high affinity agonist binding in cells.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
B.L.R. is an SAB member of Escient, Septerna and Lassogen and UNC has licensed technology from his lab to many biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

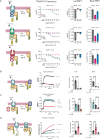

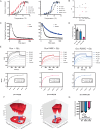

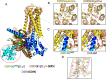
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01HL059949/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)
- R01LM013876/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | U.S. National Library of Medicine (NLM)
- F32 NS124758/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 LM013876/LM/NLM NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH112205/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM117923/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA055656/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- F32NS124758/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS)
- R35GM127303/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)
- F31 AA027949/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- U10 AA008401/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA036596/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R35 GM118105/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- F31AA027949/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA)
- R35GM118105/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)
- R01AA018734/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA)
- R35 GM127303/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL059949/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01MH112205/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH)
- RO1DA036596/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA)
- R01GM117923/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)
- R01 AA018734/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- U10AA008401/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

