Urine biomarkers can predict prostate cancer and PI-RADS score prior to biopsy
- PMID: 39103428
- PMCID: PMC11300834
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-68026-1
Urine biomarkers can predict prostate cancer and PI-RADS score prior to biopsy
Abstract
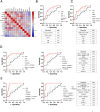
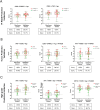
Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) based screening of prostate cancer (PCa) needs refinement. The aim of this study was the identification of urinary biomarkers to predict the Prostate Imaging-Reporting and Data System (PI-RADS) score and the presence of PCa prior to prostate biopsy. Urine samples from patients with elevated PSA were collected prior to prostate biopsy (cohort = 99). The re-analysis of mass spectrometry data from 45 samples was performed to identify urinary biomarkers to predict the PI-RADS score and the presence of PCa. The most promising candidates, i.e. SPARC-like protein 1 (SPARCL1), Lymphatic vessel endothelial hyaluronan receptor 1 (LYVE1), Alpha-1-microglobulin/bikunin precursor (AMBP), keratin 13 (KRT13), cluster of differentiation 99 (CD99) and hornerin (HRNR), were quantified by ELISA and validated in an independent cohort of 54 samples. Various biomarker combinations showed the ability to predict the PI-RADS score (AUC = 0.79). In combination with the PI-RADS score, the biomarkers improve the detection of prostate carcinoma-free men (AUC = 0.89) and of those with clinically significant PCa (AUC = 0.93). We have uncovered the potential of urinary biomarkers for a test that allows a more stringent prioritization of mpMRI use and improves the decision criteria for prostate biopsy, minimizing patient burden by decreasing the number of unnecessary prostate biopsies.
Keywords: Early detection; Non-invasive; PI-RADS score; PSA; Prostate biopsy; Prostate cancer; Prostate specific antigen; Screening of prostate cancer; Urinary biomarker; mpMRI.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Patents: This study was submitted for patent application (applicant: University of Zürich; inventors: I. Banzola, N. Alijaj, B. Pavlovic, D. Eberli). The patent application was submitted to the European patent office (application number: PCT/EP2022/086491). Conflicts of interest: N.J.R. discloses an advisory board function and receipt of honoraria from F. Hoffmann-La Roche AG. This study was submitted for patent application (applicant: University of Zürich; inventors: I. Banzola, N. Alijaj, B. Pavlovic, D. Eberli). The patent application was submitted to the European patent office (PCT/EP2022/086491). I. Banzola is founder and CEO of ONtrack Biomedical AG, a spin-off company of the University of Zurich and University Hospital Zurich, dedicated to developing PCa diagnostics. D. Eberli is also a founder of ONtrack Biomedical AG. Other authors do not have any conflict of interest.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

