Controlled labelling of tracer antibodies for time-resolved fluorescence-based immunoassays
- PMID: 39103434
- PMCID: PMC11300886
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-69294-7
Controlled labelling of tracer antibodies for time-resolved fluorescence-based immunoassays
Abstract
Tracer antibodies, which are labelled with fluorescent or other type of reporter molecules, are widely employed in diagnostic immunoassays. Time-resolved fluorescence immunoassay (TRFIA), recognized as one of the most sensitive immunoassay techniques, utilizes tracers labelled with lanthanide ion (Ln) chelates. The conventional approach for conjugating isothiocyanate (ITC) Ln-chelates to antibodies involves random chemical targeting of the primary amino group of Lys residues, requiring typically overnight exposure to an elevated pH of 9-9.3 and leading to heterogeneity. Moreover, efforts to enhance the sensitivity of the assays by introducing a higher number of Ln-chelates per tracer antibody are associated with an elevated risk of targeting critical amino acid residues in the binding site, compromising the binding properties of the antibody. Herein, we report a method to precisely label recombinant antibodies with a defined number of Ln-chelates in a well-controlled manner by employing the SpyTag/SpyCatcher protein ligation technology. We demonstrate the functionality of the method with a full-length recombinant antibody (IgG) as well as an antibody fragment by producing site-specifically labelled antibodies for TRFIA for cardiac troponin I (cTnI) detection with a significant improvement in assay sensitivity compared to that with conventionally labelled tracer antibodies. Overall, our data clearly illustrates the benefits of the site-specific labelling strategy for generating high-performing tracer antibodies for TRF immunoassays.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
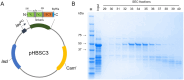
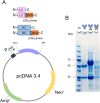
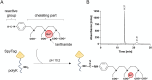
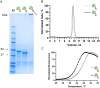
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

