Link between remnant cholesterol and the reversion to normoglycemia in Chinese adults with prediabetes: a 5-year cohort study
- PMID: 39103476
- PMCID: PMC11300864
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-69169-x
Link between remnant cholesterol and the reversion to normoglycemia in Chinese adults with prediabetes: a 5-year cohort study
Abstract
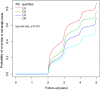
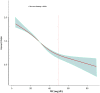
Despite the clear association between remnant cholesterol (RC)and diabetes risk, no study to date has examined the relationship between RC and reversal of prediabetes to normoglycemia. This retrospective cohort study included a total of 15,023 patients with prediabetes who underwent a physical examination between 2010 and 2016. The link between initial RC levels and the reversion from prediabetes to normoglycemia was analyzed using the Cox proportional-hazards regression model. Additionally, the study explored the possible relationship between RC and the probability of returning normoglycemia by applying Cox proportional hazards regression models with cubic spline functions. To address competing risks, a multivariate Cox regression analysis was undertaken, treating the onset of diabetes as a competing risk event for reversing prediabetes to normoglycemia. Additionally, the study incorporated extensive subgroup analyses alongside multiple sensitivity analyses, enhancing the reliability and robustness of the results. After adjusting for covariates, the findings indicated that RC was inversely associated with the likelihood of reverting to normoglycemia (per 5 mg/dL increase, HR = 0.918, 95% CI 0.909-0.927). The analysis also revealed a nonlinear relationship between RC and normoglycemia reversion, with an inflection point at 51.08 mg/dL. For RC values below this inflection point (RC < 50.08 mg/dL), the HR for the probability of returning to normoglycemia was 0.907 (95% CI 0.897-0.917 per 5 mg/dL). Additionally, the competing risks model demonstrated a negative relationship between RC and the reversal of prediabetes to normoglycemia (SHR = 0.92, 95% CI 0.91-0.93). Sensitivity analyses confirmed the robustness and stability of these results. This study demonstrated a negative and non-linear association between RC and the probability of reversion to normoglycemia in Chinese adults with prediabetes. By actively intervening to reduce RC levels, at least to below 51.08 mg/dL, further reduction of RC may significantly increase the probability of returning to normoglycemia from prediabetes.
Keywords: Competing risks model; Non-linear; Prediabetes; Remnant cholesterol; Reversion to normoglycemia.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Garber, A. J. et al. Diagnosis and management of prediabetes in the continuum of hyperglycemia: When do the risks of diabetes begin? A consensus statement from the American College of Endocrinology and the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists. Endocr. Pract.14, 933–946 (2008). 10.4158/EP.14.7.933 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

