p16-dependent increase of PD-L1 stability regulates immunosurveillance of senescent cells
- PMID: 39103548
- PMCID: PMC11321988
- DOI: 10.1038/s41556-024-01465-0
p16-dependent increase of PD-L1 stability regulates immunosurveillance of senescent cells
Abstract
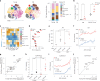
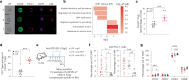
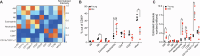
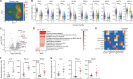
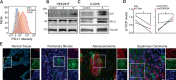
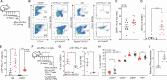
The accumulation of senescent cells promotes ageing and age-related diseases, but molecular mechanisms that senescent cells use to evade immune clearance and accumulate in tissues remain to be elucidated. Here we report that p16-positive senescent cells upregulate the immune checkpoint protein programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) to accumulate in ageing and chronic inflammation. We show that p16-mediated inhibition of cell cycle kinases CDK4/6 induces PD-L1 stability in senescent cells via downregulation of its ubiquitin-dependent degradation. p16-expressing senescent alveolar macrophages elevate PD-L1 to promote an immunosuppressive environment that can contribute to an increased burden of senescent cells. Treatment with activating anti-PD-L1 antibodies engaging Fcγ receptors on effector cells leads to the elimination of PD-L1 and p16-positive cells. Our study uncovers a molecular mechanism of p16-dependent regulation of PD-L1 protein stability in senescent cells and reveals the potential of targeting PD-L1 to improve immunosurveillance of senescent cells and ameliorate senescence-associated inflammation.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
J.M., A.A., A.M., U.A. and V.K. are co-inventors on provisional patent application related to the topic of this study. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

