Clinical and neurophysiological effects of bilateral repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation and EEG-guided neurofeedback in Parkinson's disease: a randomized, four-arm controlled trial
- PMID: 39103947
- PMCID: PMC11299373
- DOI: 10.1186/s12984-024-01427-5
Clinical and neurophysiological effects of bilateral repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation and EEG-guided neurofeedback in Parkinson's disease: a randomized, four-arm controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (rTMS) and EEG-guided neurofeedback techniques can reduce motor symptoms in Parkinson's disease (PD). However, the effects of their combination are unknown. Our objective was to determine the immediate and short-term effects on motor and non-motor symptoms, and neurophysiological measures, of rTMS and EEG-guided neurofeedback, alone or combined, compared to no intervention, in people with PD.
Methods: A randomized, single-blinded controlled trial with 4 arms was conducted. Group A received eight bilateral, high-frequency (10 Hz) rTMS sessions over the Primary Motor Cortices; Group B received eight 30-minute EEG-guided neurofeedback sessions focused on reducing average bilateral alpha and beta bands; Group C received a combination of A and B; Group D did not receive any therapy. The primary outcome measure was the UPDRS-III at post-intervention and two weeks later. Secondary outcomes were functional mobility, limits of stability, depression, health-related quality-of-life and cortical silent periods. Treatment effects were obtained by longitudinal analysis of covariance mixed-effects models.
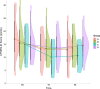
Results: Forty people with PD participated (27 males, age = 63 ± 8.26 years, baseline UPDRS-III = 15.63 ± 6.99 points, H&Y = 1-3). Group C showed the largest effect on motor symptoms, health-related quality-of-life and cortical silent periods, followed by Group A and Group B. Negligible differences between Groups A-C and Group D for functional mobility or limits of stability were found.
Conclusions: The combination of rTMS and EEG-guided neurofeedback diminished overall motor symptoms and increased quality-of-life, but this was not reflected by changes in functional mobility, postural stability or depression levels.
Trial registration: NCT04017481.
Keywords: EEG; Motor symptoms; Neurofeedback; Non-invasive neuromodulation; Parkinson’s disease; Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Cosentino G, Todisco M, Blandini F. Chapter 12 - Noninvasive neuromodulation in Parkinson’s disease: neuroplasticity implication and therapeutic perspectives. In: Quartarone A, Ghilardi MF, Boller F, editors. Handb Clin Neurol. 2022;85–98. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
- DPI2015-68664-C4-3-R (MINECO/FEDER)/Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad
- DPI2015-68664-C4-1-R (MINECO/FEDER)/Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad
- DPI2015-68664-C4-1-R (MINECO/FEDER)/Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad
- DPI2015-68664-C4-1-R (MINECO/FEDER)/Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad
- PID2020-113222RBC21/AEI/10.13039/501100011033/Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

