The Icelandic Heart Failure Registry-A nationwide assessment tool for HF care and intervention in HF treatment
- PMID: 39104306
- PMCID: PMC11631331
- DOI: 10.1002/ehf2.15012
The Icelandic Heart Failure Registry-A nationwide assessment tool for HF care and intervention in HF treatment
Abstract
Introduction: The incidence of heart failure (HF) is increasing, largely because populations are both ageing and growing. Most clinical HF treatment trials are conducted on selected cohorts, only a few of which include elderly patients, among whom HF is common. HF registries can include all HF patients, independent of age or comorbidity profile, and thus reflect reality in healthcare management.
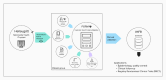
Methods: The Icelandic Heart Failure Registry (IHFR) was created in the autumn of 2019 and has operated since 1 January 2020. Based on the Swedish Heart Failure Registry (SwedeHF), it quickly acquired several extensions. All patients admitted for HF to the Department of Cardiology (DC) at Landspítali - The National University Hospital of Iceland are included. Several variables are collected, including the aetiology of HF, comorbidities, clinical assessment at admission, blood tests, imaging results, treatment given and medical therapy at discharge.
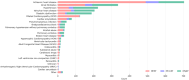
Results: During the 3 years from 2020 to 2022, the DC admitted 1890 patients. As some were readmitted during the study period, the true total was 2384 admissions. Because the IHFR 2023 edition includes 327 variables, automation of many of them is imperative for data collection.
Conclusion: HF is a heterogenous disease with numerous underlying factors. HF management differs among HF phenotypes. A registry can serve as an unbiased indicator of care quality and has the potential to be studied in the future to assess the long-term effects of HF treatment. A registry like the IHFR, therefore, can impact the treatment of all patients recorded in it, reduce the rate of readmissions and even optimize HF management costs.
Keywords: heart failure outcomes; heart failure phenotypes; quality of care; registry.
© 2024 The Author(s). ESC Heart Failure published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of European Society of Cardiology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

