Recent deep learning-based brain tumor segmentation models using multi-modality magnetic resonance imaging: a prospective survey
- PMID: 39104626
- PMCID: PMC11298476
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1392807
Recent deep learning-based brain tumor segmentation models using multi-modality magnetic resonance imaging: a prospective survey
Abstract
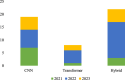
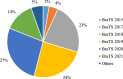
Radiologists encounter significant challenges when segmenting and determining brain tumors in patients because this information assists in treatment planning. The utilization of artificial intelligence (AI), especially deep learning (DL), has emerged as a useful tool in healthcare, aiding radiologists in their diagnostic processes. This empowers radiologists to understand the biology of tumors better and provide personalized care to patients with brain tumors. The segmentation of brain tumors using multi-modal magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) images has received considerable attention. In this survey, we first discuss multi-modal and available magnetic resonance imaging modalities and their properties. Subsequently, we discuss the most recent DL-based models for brain tumor segmentation using multi-modal MRI. We divide this section into three parts based on the architecture: the first is for models that use the backbone of convolutional neural networks (CNN), the second is for vision transformer-based models, and the third is for hybrid models that use both convolutional neural networks and transformer in the architecture. In addition, in-depth statistical analysis is performed of the recent publication, frequently used datasets, and evaluation metrics for segmentation tasks. Finally, open research challenges are identified and suggested promising future directions for brain tumor segmentation to improve diagnostic accuracy and treatment outcomes for patients with brain tumors. This aligns with public health goals to use health technologies for better healthcare delivery and population health management.
Keywords: brain tumor segmentation; convolutional neural network; deep learning; medical images; multi-modality analysis; vision transformers.
Copyright © 2024 Abidin, Naqvi, Haider, Kim, Jeong and Lee.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures



References
-
- Akbar A. S., Fatichah C., Suciati N. (2021). “Unet3d with multiple atrous convolutions attention block for brain tumor segmentation,” in International MICCAI brainlesion w orkshop (Springer; ), 182–193.
-
- Ali S., Li J., Pei Y., Khurram R., Rehman K. u., Mahmood T. (2022). A comprehensive survey on brain tumor diagnosis using deep learning and emerging hybrid techniques with multi-modal mr image. Archives Comput. methods Eng. 29, 4871–4896. 10.1007/s11831-022-09758-z - DOI
-
- Amiri S., Ibragimov B. (2022). Improved automated lesion segmentation in whole-body fdg/pet-ct via test-time augmentation. arXiv Prepr. arXiv:2210.07761. 10.48550/arXiv.2210.07761 - DOI
-
- Ancona M., Ceolini E., Öztireli C., Gross M. (2017). Towards a better understanding of gradient-based attribution methods for deep neural networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1711.06104.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

