Closed-Loop Insulin Therapy for People With Type 2 Diabetes Treated With an Insulin Pump: A 12-Week Multicenter, Open-Label Randomized, Controlled, Crossover Trial
- PMID: 39106206
- PMCID: PMC11417293
- DOI: 10.2337/dc24-0623
Closed-Loop Insulin Therapy for People With Type 2 Diabetes Treated With an Insulin Pump: A 12-Week Multicenter, Open-Label Randomized, Controlled, Crossover Trial
Abstract
Objective: Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) combined with continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion (CSII) achieves better glycemic control than multi-injection therapy in people with type 2 diabetes. The effectiveness of closed-loop therapy needs to be further evaluated in this population.
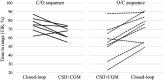
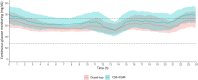
Research design and methods: The study objective was to measure the impact of a hybrid closed-loop device (DBLG1) compared with CSII + CGM on glycemic control in people with type 2 diabetes previously treated with CSII. The randomized, controlled, crossover, two-period, open-label, and multicenter study was conducted from August 2022 to July 2023 in 17 individuals (9 to receive 6 weeks of CSII + CGM first and 8 to receive 6 weeks of closed-loop therapy first). The primary end point was the percentage time in range (TIR: 70-180 mg/dL). Secondary outcomes were other CGM-glucose metrics, physical activity, and sleep objectively measured using 1-week actimetry.
Results: Data were analyzed using a modified intention-to-treat approach. Mean age was 63 (SD 9) years and 35% were women. Mean HbA1c at inclusion was 7.9% (SD 0.9). TIR increased to 76.0% (interquartile range 69.0-84.0) during the closed-loop condition vs. 61.0% (interquartile range 55.0-70.0) during the CSII + CGM condition; mean difference was 15.0 percentage points (interquartile range 8.0-22.0; P < 0.001). Analyses of secondary end points showed a decrease in time above range, in glucose management indicator, in glucose variability, and an increase in daily insulin dose. Actimetric sleep analysis showed an improvement in sleep fragmentation during closed-loop treatment.
Conclusions: Closed-loop therapy improved glycemic control more than did CSII + CGM in people with type 2 diabetes.
© 2024 by the American Diabetes Association.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Magliano DJ, Boyko E.J. IDF Diabetes Atlas. 10th ed. Brussels, 2021.
-
- Tancredi M, Rosengren A, Svensson A-M, et al. Excess mortality among persons with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2015;373:1720–1732 - PubMed
-
- Fosse-Edorh SPC, Saboni L, Mandereau-Bruno L, et al. Études Entred: un dispositif pour améliorer la connaissance de l’état de santé des personnes présentant un diabète en France – Premiers résultats de la troisième édition conduite en métropole en 2019. Bull Epidémiol Hebd 2022;22:383–392
-
- Reznik Y, Cohen O, Aronson R, et al. ; OpT2mise Study Group . Insulin pump treatment compared with multiple daily injections for treatment of type 2 diabetes (OpT2mise): a randomised open-label controlled trial. Lancet 2014;384:1265–1272 - PubMed
-
- Bétry C, Lablanche S, Carvalho M, et al. Effect of a lifestyle intervention to prevent weight gain at initiation of insulin pump therapy in type 2 diabetes: A randomized, controlled, multicentre trial. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2023;200:110698. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical