Combination of radiotherapy and PD-L1 blockade induces abscopal responses in EGFR-mutated lung cancer through activating CD8+ T cells
- PMID: 39106551
- PMCID: PMC11357862
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tranon.2024.102074
Combination of radiotherapy and PD-L1 blockade induces abscopal responses in EGFR-mutated lung cancer through activating CD8+ T cells
Abstract
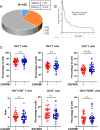
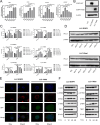
Patients with EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) respond poorly to immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs). It has been reported that the number of CD8+T cells is reduced in EGFR-mutated NSCLC. However, the extent of heterogeneity and effector function of distinct populations of CD8+T cells has not been investigated intensively. In addition, studies investigating whether a combination of radiotherapy and ICIs can improve the efficacy of ICIs in EGFR-mutated lung cancer are lacking. Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) was used to investigate the heterogeneity of CD8+T cell populations in EGFR-mutated NSCLC. The STING pathway was explored after hypofractionated radiation of EGFR-mutated and wild-type cells. Mice bearing LLC-19del and LLC-EGFR tumors were treated with radiotherapy plus anti-PD-L1. The scRNA-seq data showed the percentage of progenitor exhausted CD8+T cells was lower in EGFR-mutated NSCLC. In addition, CD8+T cells in EGFR-mutated NSCLC were enriched in oxidative phosphorylation. In EGFR-mutated and wild-type cells, 8 Gy × 3 increased the expression of chemokines that recruit T cells and activate the cGAS-STING pathway. In the LLC-19del and LLC-EGFR mouse model, the combination of radiation and anti-PD-L1 significantly inhibited the growth of abscopal tumors. The enhanced abscopal effect was associated with systemic CD8+T cell infiltration. This study provided an intensive understanding of the heterogeneity and effector functions of CD8+T cells in EGFR-mutated NSCLC. We showed that the combination of hypofractionated radiation and anti-PD-L1 significantly enhanced the abscopal responses in both EGFR-mutated and wild-type lung cancer by activating CD8+T cells in mice.
Keywords: Abscopal effect; Anti-PD-L1; Epidermal growth factor receptor; Radiotherapy; Single-cell RNA sequencing.
Copyright © 2024. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




References
-
- Shi Y., Au J.S., Thongprasert S., Srinivasan S., Tsai C.M., Khoa M.T., Heeroma K., Itoh Y., Cornelio G., Yang P.C. A prospective, molecular epidemiology study of EGFR mutations in Asian patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer of adenocarcinoma histology (PIONEER) J. Thorac. Oncol. 2014;9(2):154–162. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0000000000000033. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Reck M., Rodriguez-Abreu D., Robinson A.G., Hui R., Csoszi T., Fulop A., Gottfried M., Peled N., Tafreshi A., Cuffe S., O'Brien M., Rao S., Hotta K., Leiby M.A., Lubiniecki G.M., Shentu Y., Rangwala R., Brahmer J.R., Investigators K. Pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy for PD-L1-positive non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016;375(19):1823–1833. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1606774. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lee C.K., Man J., Lord S., Cooper W., Links M., Gebski V., Herbst R.S., Gralla R.J., Mok T., Yang J.C. Clinical and molecular characteristics associated with survival among patients treated with checkpoint inhibitors for advanced non-small cell lung carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Oncol. 2018;4(2):210–216. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2017.4427. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

