Rapid retinoic acid-induced trophoblast cell model from human induced pluripotent stem cells
- PMID: 39107470
- PMCID: PMC11303561
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-68952-0
Rapid retinoic acid-induced trophoblast cell model from human induced pluripotent stem cells
Abstract
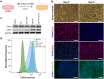
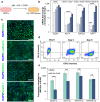
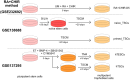
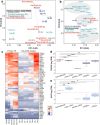
A limited number of accessible and representative models of human trophoblast cells currently exist for the study of placentation. Current stem cell models involve either a transition through a naïve stem cell state or precise dynamic control of multiple growth factors and small-molecule cues. Here, we demonstrated that a simple five-day treatment of human induced pluripotent stem cells with two small molecules, retinoic acid (RA) and Wnt agonist CHIR 99021 (CHIR), resulted in rapid, synergistic upregulation of CDX2. Transcriptomic analysis of RA + CHIR-treated cells showed high similarity to primary trophectoderm cells. Multipotency was verified via further differentiation towards cells with syncytiotrophoblast or extravillous trophoblast features. RA + CHIR-treated cells were also assessed for the established criteria defining a trophoblast cell model, and they possess all the features necessary to be considered valid. Collectively, our data demonstrate a facile, scalable method for generating functional trophoblast-like cells in vitro to better understand the placenta.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
K.A.L., C.A.S., and S.M.A. have a patent pending for the methods described herein to establish the trophoblast model.
Figures
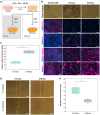
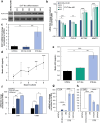
Similar articles
-
Two distinct trophectoderm lineage stem cells from human pluripotent stem cells.J Biol Chem. 2021 Jan-Jun;296:100386. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100386. Epub 2021 Feb 5. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33556374 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of CDX2 and EOMES in human induced trophoblast progenitor cells.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013 Feb 8;431(2):197-202. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.12.135. Epub 2013 Jan 8. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013. PMID: 23313847 Free PMC article.
-
Human pluripotent stem cells as a model of trophoblast differentiation in both normal development and disease.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Jul 5;113(27):E3882-91. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1604747113. Epub 2016 Jun 20. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27325764 Free PMC article.
-
Early differentiation and gene expression characteristics of trophoblast lineages†.Biol Reprod. 2023 May 10;108(5):709-719. doi: 10.1093/biolre/ioad027. Biol Reprod. 2023. PMID: 36892411 Review.
-
Breaking the first lineage barrier - many roads to trophoblast stem cell fate.Placenta. 2017 Dec;60 Suppl 1:S52-S56. doi: 10.1016/j.placenta.2016.12.025. Epub 2016 Dec 23. Placenta. 2017. PMID: 28043657 Review.
References
-
- Latos, P. A. & Hemberger, M. From the stem of the placental tree: Trophoblast stem cells and their progeny. Dev. Camb.143, 3650–3660 (2016). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

