A pre-vertebrate endodermal origin of calcitonin-producing neuroendocrine cells
- PMID: 39109637
- PMCID: PMC11698069
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.202821
A pre-vertebrate endodermal origin of calcitonin-producing neuroendocrine cells
Abstract
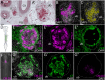
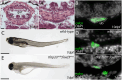
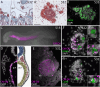
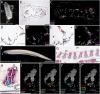
Vertebrate calcitonin-producing cells (C-cells) are neuroendocrine cells that secrete the small peptide hormone calcitonin in response to elevated blood calcium levels. Whereas mouse C-cells reside within the thyroid gland and derive from pharyngeal endoderm, avian C-cells are located within ultimobranchial glands and have been reported to derive from the neural crest. We use a comparative cell lineage tracing approach in a range of vertebrate model systems to resolve the ancestral embryonic origin of vertebrate C-cells. We find, contrary to previous studies, that chick C-cells derive from pharyngeal endoderm, with neural crest-derived cells instead contributing to connective tissue intimately associated with C-cells in the ultimobranchial gland. This endodermal origin of C-cells is conserved in a ray-finned bony fish (zebrafish) and a cartilaginous fish (the little skate, Leucoraja erinacea). Furthermore, we discover putative C-cell homologs within the endodermally-derived pharyngeal epithelium of the ascidian Ciona intestinalis and the amphioxus Branchiostoma lanceolatum, two invertebrate chordates that lack neural crest cells. Our findings point to a conserved endodermal origin of C-cells across vertebrates and to a pre-vertebrate origin of this cell type along the chordate stem.
Keywords: Calcitonin; Endoderm; Evolution; Neural crest; Neuroendocrine.
© 2024. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests È.B.-G. has been employed by Genentech since September 2022. The rest of the authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Andrew, A. (1974). Further evidence that enterochromaffin cells are not derived from the neural crest. J. Embryol. Exp. Morphol. 31, 589-598. - PubMed
-
- Andrews, T. G. R., Gattoni, G., Busby, L., Schwimmer, M. A. and Benito-Gutierrez, È (2020). Hybridization chain reaction for quantitative and multiplex imaging of gene expression in amphioxus embryos and adult tissues. Methods Mol. Biol. 2148, 179-194. 10.1007/978-1-0716-0623-0_11 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K99 DE029858/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01MH113362/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- 214953/Z/18/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R35 DE027550/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- E.J. Whitten Foundation
- T32 GM008554/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- F31 DE030007/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- T32GM008554/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH113362/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- UF130182/Royal Society
- F31DE030007/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- C9545/A29580/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- Marine Biological Laboratory
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

