Development and Application of a Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry Method for the Analysis of 20 Perfluoroalkyl Substances in Fruit and Vegetables at Sub-Parts-per-Trillion Levels
- PMID: 39109800
- PMCID: PMC11342373
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jafc.4c01172
Development and Application of a Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry Method for the Analysis of 20 Perfluoroalkyl Substances in Fruit and Vegetables at Sub-Parts-per-Trillion Levels
Abstract
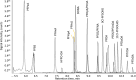
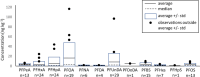
In response to the European Food Safety Authority's establishment of a tolerable weekly intake (TWI) for the sum of PFOA, PFNA, PFHxS, and PFOS, a method was developed to quantify and confirm 20 PFASs at the sub-parts-per-trillion level in fruit and vegetables. Improved sensitivity was achieved by (i) increasing the sample intake, (ii) decreasing the solvent volume in the final extract, and (iii) using a highly sensitive mass spectrometer. Except for PFTrDA, target PFASs could be quantitatively determined with an apparent recovery of 90-119%, limits of quantitation down to 0.5 ng/kg, and a relative standard deviation under within-laboratory reproducibility conditions of <28%. The method was successfully applied to 215 fruit and vegetable samples obtained from local grocery stores and markets. Leafy vegetables prove to be the main vegetable category responsible to PFAS exposure, mainly of PFOA, followed by PFHpA and PFHxA.
Keywords: LC−MS/MS; PFASs; exposure; food; validation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

References
-
- Buck R. C.; Franklin J.; Berger U.; Conder J. M.; Cousins I. T.; De Voogt P.; Jensen A. A.; Kannan K.; Mabury S. A.; Van Leeuwen S. P. Perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances in the environment: Terminology, classification, and origins. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manage. 2011, 7 (4), 513–541. 10.1002/ieam.258. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Schrenk D.; Bignami M.; Bodin L.; Chipman J. K.; del Mazo J.; Grasl-Kraupp B.; Hogstrand C.; Hoogenboom L. R.; Leblanc J.-C.; Nebbia C. S.; Nielsen E.; Ntzani E.; Petersen A.; Sand S.; Vleminckx C.; Wallace H.; Barregård L.; Ceccatelli S.; Cravedi J.-P.; Halldorsson T. I.; Haug L. S.; Johansson N.; Knutsen H. K.; Rose M.; Roudot A.-C.; Van Loveren H.; Vollmer G.; Mackay K.; Riolo F.; Schwerdtle T. Risk to human health related to the presence of perfluoroalkyl substances in food. EFSA J. 2020, 18 (9), 6223.10.2903/j.efsa.2020.6223. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- European Union Reference Laboratory for Halogenated Persistent Organic Pollutants in Feed and Food (EURL-POPs) . Guidance Document on Analytical Parameters for the Determination of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Food and Feed; EURL-POPs: Baden-Wuerttemberg, Germany, 2022; https://eurl-pops.eu/news/guidance-document-pfas/guidance-document-pfas.
-
- Commission Recommendation (EU) 2022/1431 of 24 August 2022 on the monitoring of perfluoroalkyl substances in food. Off. J. Eur. Union 2022, 221, 105–109.
-
- Jiménez-Skrzypek G.; González-Sálamo J.; Hernández-Borges J. Analytical methodologies and occurrence of per- and polyfluorinated alkyl substances—A review. J. Chromatogr. Open 2023, 4, 100089.10.1016/j.jcoa.2023.100089. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

