Antitumorigenic potential of Lactobacillus-derived extracellular vesicles: p53 succinylation and glycolytic reprogramming in intestinal epithelial cells via SIRT5 modulation
- PMID: 39110260
- PMCID: PMC11306434
- DOI: 10.1007/s10565-024-09897-y
Antitumorigenic potential of Lactobacillus-derived extracellular vesicles: p53 succinylation and glycolytic reprogramming in intestinal epithelial cells via SIRT5 modulation
Abstract
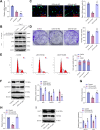
Objective: Colorectal cancer progression involves complex cellular mechanisms. This study examines the effects of Lactobacillus plantarum-derived extracellular vesicles (LEVs) on the SIRT5/p53 axis, focusing on glycolytic metabolic reprogramming and abnormal proliferation in intestinal epithelial cells.
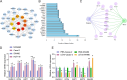
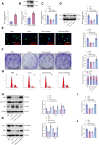
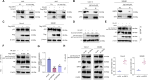
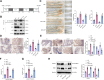
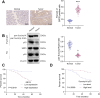
Methods: LEVs were isolated from Lactobacillus plantarum and incubated with Caco-2 cells. Differential gene expression was analyzed through RNA sequencing and compared with TCGA-COAD data. Key target genes and pathways were identified using PPI network and pathway enrichment analysis. Various assays, including RT-qPCR, EdU staining, colony formation, flow cytometry, and Western blotting, were used to assess gene expression, cell proliferation, and metabolic changes. Co-immunoprecipitation confirmed the interaction between SIRT5 and p53, and animal models were employed to validate in vivo effects.
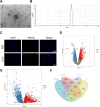
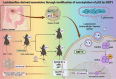
Results: Bioinformatics analysis indicated the SIRT5/p53 axis as a critical pathway in LEVs' modulation of colorectal cancer. LEVs were found to inhibit colorectal cancer cell proliferation and glycolytic metabolism by downregulating SIRT5, influencing p53 desuccinylation. In vivo, LEVs regulated this axis, reducing tumor formation in mice. Clinical sample analysis showed that SIRT5 and p53 succinylation levels correlated with patient prognosis.
Conclusion: Lactobacillus-derived extracellular vesicles play a pivotal role in suppressing colonic tumor formation by modulating the SIRT5/p53 axis. This results in decreased glycolytic metabolic reprogramming and reduced proliferation in intestinal epithelial cells.
Keywords: Lactobacillus; Colorectal cancer; Extracellular vesicles; Palmitoylation modification; SIRT5; p53.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

