Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of neurally mediated syncope in children and adolescents (revised 2024)
- PMID: 39110332
- PMCID: PMC11502568
- DOI: 10.1007/s12519-024-00819-w
Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of neurally mediated syncope in children and adolescents (revised 2024)
Abstract
Background: Significant progress has been made in the diagnosis and treatment of pediatric syncope since the publication of the "2018 Chinese Pediatric Cardiology Society (CPCS) guideline for diagnosis and treatment of syncope in children and adolescents" ("2018 Edition Guidelines"). Therefore, we have revised and updated it to assist pediatricians in effectively managing children with syncope.
Data sources: According to the "2018 Edition Guidelines", the expert groups collected clinical evidence, evaluated preliminary recommendations, and then organized open-ended discussions to form the recommendations. This guideline was developed by reviewing the literature and studies in databases including PubMed, Cochrane, EMBASE, China Biomedical Database, and Chinese Journal Full-text Database up to April 2024. Search terms included "syncope", "children", "adolescents", "diagnosis", and "treatment."
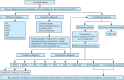
Results: The guidelines were based on the latest global research progress and were evidence-based. The classification of syncope etiology, diagnostic procedures, postural tests, such as the active standing test, head-up tilt test, and active sitting test, clinical diagnosis, and individualized treatment for neurally mediated syncope in pediatric population were included.
Conclusions: The guidelines were updated based on the latest literature. The concepts of sitting tachycardia syndrome and sitting hypertension were introduced and the comorbidities of neurally mediated syncope were emphasized. Some biomarkers used for individualized treatment were underlined. Specific suggestions were put forward for non-pharmacological therapies as well as the follow-up process. The new guidelines will provide comprehensive guidance and reference for the diagnosis and treatment of neurally mediated syncope in children and adolescents.
Keywords: Adolescents; Children; Diagnosis; Neurally mediated syncope; Treatment.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
No financial or non-financial benefits have been received or will be received from any party related directly or indirectly to the subject of this article. Author Jun-Bao Du is a member of the Editorial Board for
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

