Saponin nanoparticle adjuvants incorporating Toll-like receptor agonists drive distinct immune signatures and potent vaccine responses
- PMID: 39110802
- PMCID: PMC11305391
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adn7187
Saponin nanoparticle adjuvants incorporating Toll-like receptor agonists drive distinct immune signatures and potent vaccine responses
Abstract
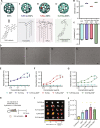
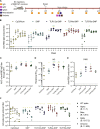
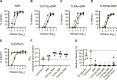
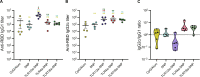
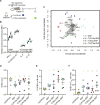
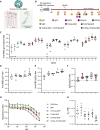
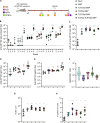
Over the past few decades, the development of potent and safe immune-activating adjuvant technologies has become the heart of intensive research in the constant fight against highly mutative and immune evasive viruses such as influenza, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). Herein, we developed a highly modular saponin-based nanoparticle platform incorporating Toll-like receptor agonists (TLRas) including TLR1/2a, TLR4a, and TLR7/8a adjuvants and their mixtures. These various TLRa-saponin nanoparticle adjuvant constructs induce unique acute cytokine and immune-signaling profiles, leading to specific T helper responses that could be of interest depending on the target disease for prevention. In a murine vaccine study, the adjuvants greatly improved the potency, durability, breadth, and neutralization of both COVID-19 and HIV vaccine candidates, suggesting the potential broad application of these adjuvant constructs to a range of different antigens. Overall, this work demonstrates a modular TLRa-SNP adjuvant platform that could improve the design of vaccines and affect modern vaccine development.
Figures
Update of
-
Saponin Nanoparticle Adjuvants Incorporating Toll-Like Receptor Agonists Drive Distinct Immune Signatures and Potent Vaccine Responses.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jun 27:2023.07.16.549249. doi: 10.1101/2023.07.16.549249. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Sci Adv. 2024 Aug 9;10(32):eadn7187. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adn7187. PMID: 37577608 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Moyle P. M., Toth I., Modern subunit vaccines: Development, components, and research opportunities. ChemMedChem 8, 360–376 (2013). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

