The Application of a Serious Game Framework to Design and Develop an Exergame for Patients With Heart Failure
- PMID: 39110976
- PMCID: PMC11339584
- DOI: 10.2196/50063
The Application of a Serious Game Framework to Design and Develop an Exergame for Patients With Heart Failure
Abstract
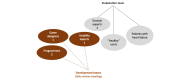
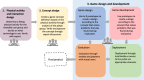
Reducing inactivity in patients with chronic disease is vital since it can decrease the risk of disease progression and mortality. Exergames are an innovative approach to becoming more physically active and positively affecting physical health outcomes. Serious games are designed for purposes beyond entertainment and exergames are serious games for physical activity. However, current commercial exergames might not optimally meet the needs of patients with special needs. Developing tailored exergames is challenging and requires an appropriate process. The primary goal of this viewpoint is to describe significant lessons learned from designing and developing an exergame for patients with chronic heart failure using the player-centered, iterative, interdisciplinary, and integrated (P-III) framework for serious games. Four of the framework's pillars were used in the design and development of a mobile exergame: player-centered design, iterative development of the game, interdisciplinary teamwork, and integration of play and serious content. The mobile exergame was developed iteratively in 7 iterations by an interdisciplinary team involving users and stakeholders in all iterations. Stakeholders played various roles during the development process, making the team stay focused on the needs of the patients and creating an exergame that catered to these needs. Evaluations were conducted during each iteration by both the team and users or patients according to the player-centered design pillar. Since the exergame was created for a smartphone, the assessments were conducted both on the development computer and on the intended platforms. This required continuous deployment of the exergame to the platforms and smartphones that support augmented reality. Our findings show that the serious game P-III framework needs to be modified in order to be used for the design and development of exergames. In this viewpoint, we propose an updated version of the P-III framework for exergame development including (1) a separate and thorough design of the physical activity and physical interaction, and (2) early and continuous deployment of the exergame on the intended platform to enable evaluations and everyday life testing.
Keywords: exergames; heart failure; human-computer interaction; mobile health apps; mobile phone; physical activity; player-centered design.
©Aseel Berglund, Tiny Jaarsma, Helena Orädd, Johan Fallström, Anna Strömberg, Leonie Klompstra, Erik Berglund. Originally published in JMIR Formative Research (https://formative.jmir.org), 07.08.2024.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
Figures




References
-
- Tremblay MS, Aubert S, Barnes JD, Saunders TJ, Carson V, Latimer-Cheung AE, Chastin SF, Altenburg TM, Chinapaw MJ. Sedentary behavior research network (SBRN)—terminology consensus project process and outcome. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2017;14(1):75. doi: 10.1186/s12966-017-0525-8. https://ijbnpa.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12966-017-0525-8 10.1186/s12966-017-0525-8 - DOI - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sedentary Behaviour Research Network Letter to the editor: standardized use of the terms "sedentary" and "sedentary behaviours". Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2012;37(3):540–542. doi: 10.1139/h2012-024. https://cdnsciencepub.com/doi/abs/10.1139/h2012-024?url_ver=Z39.88-2003&... - DOI - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ekelund U, Tarp J, Steene-Johannessen J, Hansen BH, Jefferis B, Fagerland MW, Whincup P, Diaz KM, Hooker SP, Chernofsky A, Larson MG, Spartano N, Vasan RS, Dohrn I, Hagströmer M, Edwardson C, Yates T, Shiroma E, Anderssen SA, Lee I. Dose-response associations between accelerometry measured physical activity and sedentary time and all cause mortality: systematic review and harmonised meta-analysis. BMJ. 2019;366:l4570. doi: 10.1136/bmj.l4570. http://www.bmj.com/lookup/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=31434697 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Stamatakis E, Gale J, Bauman A, Ekelund U, Hamer M, Ding D. Sitting time, physical activity, and risk of mortality in adults. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019;73(16):2062–2072. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2019.02.031. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0735-1097(19)33789-1 S0735-1097(19)33789-1 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

