Intermittent clearance of p21-highly-expressing cells extends lifespan and confers sustained benefits to health and physical function
- PMID: 39111286
- PMCID: PMC11315361
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2024.07.006
Intermittent clearance of p21-highly-expressing cells extends lifespan and confers sustained benefits to health and physical function
Abstract
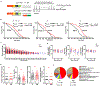
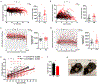
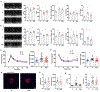
A key challenge in aging research is extending lifespan in tandem with slowing down functional decline so that life with good health (healthspan) can be extended. Here, we show that monthly clearance, starting from 20 months, of a small number of cells that highly express p21Cip1 (p21high) improves cardiac and metabolic function and extends both median and maximum lifespans in mice. Importantly, by assessing the health and physical function of these mice monthly until death, we show that clearance of p21high cells improves physical function at all remaining stages of life, suggesting healthspan extension. Mechanistically, p21high cells encompass several cell types with a relatively conserved proinflammatory signature. Clearance of p21high cells reduces inflammation and alleviates age-related transcriptomic signatures of various tissues. These findings demonstrate the feasibility of healthspan extension in mice and indicate p21high cells as a therapeutic target for healthy aging.
Keywords: aging; cellular senescence; frailty; inflammation; morbidity compression.
Copyright © 2024 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests M.X., T.T., and J.L.K. have a financial conflict of interest with a Mayo Clinic pending patent for p21-Cre mouse model.
Figures


References
-
- Office for National Statistics, Health state life expectancies, UK: 2015 to 2017. (2018). https://www.ons.gov.uk/peoplepopulationandcommunity/healthandsocialcare/....
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AG076642/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R03 AG072374/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AG013925/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U54 AG079753/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA034196/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG013319/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG068635/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG066679/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG044271/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG067988/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R33 AG061456/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HG010463/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- F30 AG081092/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG068860/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AG071292/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG062413/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

