Predicting gestational diabetes mellitus risk at 11-13 weeks' gestation: the role of extrachromosomal circular DNA
- PMID: 39113025
- PMCID: PMC11304788
- DOI: 10.1186/s12933-024-02381-1
Predicting gestational diabetes mellitus risk at 11-13 weeks' gestation: the role of extrachromosomal circular DNA
Abstract
Background: Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) significantly impacts maternal and infant health both immediately and over the long term, yet effective early diagnostic biomarkers are currently lacking. Thus, it is essential to identify early diagnostic biomarkers for GDM risk screening. Extrachromosomal circular DNA (eccDNA), being more stable than linear DNA and involved in disease pathologies, is a viable biomarker candidate for diverse conditions. In this study, eccDNA biomarkers identified for early diagnosis and assessment of GDM risk were explored.
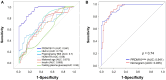
Methods: Using Circle-seq, we identified plasma eccDNA profiles in five pregnant women who later developed GDM and five matched healthy controls at 11-13 weeks of gestation. These profiles were subsequently analyzed through bioinformatics and validated through outward PCR combined with Sanger sequencing. Furthermore, candidate eccDNA was validated by quantitative PCR (qPCR) in a larger cohort of 70 women who developed GDM and 70 normal glucose-tolerant (NGT) subjects. A ROC curve assessed the eccDNA's diagnostic potential for GDM.
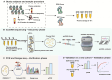
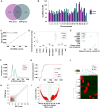
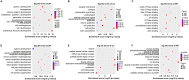
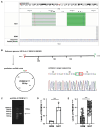
Results: 2217 eccDNAs were differentially detected between future GDM patients and controls, with 1289 increased and 928 decreased in abundance. KEGG analysis linked eccDNA genes mainly to GDM-related pathways such as Rap1, MAPK, and PI3K-Akt, and Insulin resistance, among others. Validation confirmed a significant decrease in eccDNA PRDM16circle in the plasma of 70 women who developed GDM compared to 70 NGT women, consistent with the eccDNA-seq results. PRDM16circle showed significant diagnostic value in 11-13 weeks of gestation (AUC = 0.941, p < 0.001).
Conclusions: Our study first demonstrats that eccDNAs are aberrantly produced in women who develop GDM, including PRDM16circle, which can predict GDM at an early stage of pregnancy, indicating its potential as a biomarker.
Trial registration: ChiCTR2300075971, http://www.chictr.org.cn . Registered 20 September 2023.
Keywords: Extrachromosomal circular DNA; Gestational diabetes mellitus; Predictive biomarker.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Metabolomic profiling reveals early biomarkers of gestational diabetes mellitus and associated hepatic steatosis.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025 Mar 20;24(1):125. doi: 10.1186/s12933-025-02645-4. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025. PMID: 40114104 Free PMC article.
-
Differential expression and analysis of extrachromosomal circular DNAs as serum biomarkers in pulmonary arterial hypertension.Respir Res. 2024 Apr 25;25(1):181. doi: 10.1186/s12931-024-02808-z. Respir Res. 2024. PMID: 38664836 Free PMC article.
-
Increased serum extrachromosomal circular DNA SORBS1circle level is associated with insulin resistance in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2024 Jan 12;29(1):12. doi: 10.1186/s11658-023-00530-0. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2024. PMID: 38212723 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Early Pregnancy Risk Prediction Model for Gestational Diabetes Mellitus.Fetal Diagn Ther. 2019;45(2):76-84. doi: 10.1159/000486853. Epub 2018 Jun 13. Fetal Diagn Ther. 2019. PMID: 29898442 Review.
-
Screening and diagnosing gestational diabetes mellitus.Evid Rep Technol Assess (Full Rep). 2012 Oct;(210):1-327. Evid Rep Technol Assess (Full Rep). 2012. PMID: 24423035 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
tRF-5028c disrupts trophoblast function in recurrent spontaneous abortion by inhibiting CRKL-mediated Rap1 signaling pathway.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2025 Mar 5;30(1):28. doi: 10.1186/s11658-025-00706-w. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2025. PMID: 40045194 Free PMC article.
-
Extrachromosomal Circular DNA MIRECD Enhances Necroptosis and Predicts Prognosis of Myocardial Infarction.Research (Wash D C). 2025 Aug 8;8:0803. doi: 10.34133/research.0803. eCollection 2025. Research (Wash D C). 2025. PMID: 40785966 Free PMC article.
-
Extrachromosomal circular DNA drives dynamic genome plasticity: emerging roles in disease progression and clinical potential.Theranostics. 2025 May 25;15(13):6387-6411. doi: 10.7150/thno.111765. eCollection 2025. Theranostics. 2025. PMID: 40521196 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolomic profiling reveals early biomarkers of gestational diabetes mellitus and associated hepatic steatosis.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025 Mar 20;24(1):125. doi: 10.1186/s12933-025-02645-4. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025. PMID: 40114104 Free PMC article.
-
Extrachromosomal Circular DNA in Cancer: Mechanisms and Clinical Applications.Cell Prolif. 2025 Jun;58(6):e70040. doi: 10.1111/cpr.70040. Epub 2025 Apr 29. Cell Prolif. 2025. PMID: 40300805 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wang H, Li N, Chivese T, Werfalli M, Sun H, Yuen L, et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: estimation of global and regional gestational diabetes mellitus prevalence for 2021 by International Association of Diabetes in Pregnancy Study Group’s criteria. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2022;183: 109050. 10.1016/j.diabres.2021.109050 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- 202305020433/Medical and Health Science and Technology Development Project of Shandong Province
- 202328021/Science and Technology Development Project of Jinan
- 202225064/Science and Technology Development Project of Jinan
- 2023Y9384/Joint Funds for the Innovation of Science and Technology, Fujian Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

