Phase separation and transcriptional regulation in cancer development
- PMID: 39113127
- PMCID: PMC11300516
- DOI: 10.7555/JBR.37.20230214
Phase separation and transcriptional regulation in cancer development
Abstract
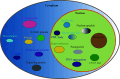
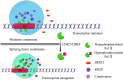
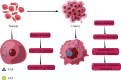
Liquid-liquid phase separation, a novel biochemical phenomenon, has been increasingly studied for its medical applications. It underlies the formation of membrane-less organelles and is involved in many cellular and biological processes. During transcriptional regulation, dynamic condensates are formed through interactions between transcriptional elements, such as transcription factors, coactivators, and mediators. Cancer is a disease characterized by uncontrolled cell proliferation, but the precise mechanisms underlying tumorigenesis often remain to be elucidated. Emerging evidence has linked abnormal transcriptional condensates to several diseases, especially cancer, implying that phase separation plays an important role in tumorigenesis. Condensates formed by phase separation may have an effect on gene transcription in tumors. In the present review, we focus on the correlation between phase separation and transcriptional regulation, as well as how this phenomenon contributes to cancer development.
Keywords: cancer; condensates; phase separation; super-enhancer; transcription regulation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors reported no conflict of interests.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources