Circ_0028826 Promotes Growth and Metastasis of NSCLC via Acting as a Sponge of miR-758-3p to Derepress IDH2 Expression
- PMID: 39113352
- PMCID: PMC11306285
- DOI: 10.1111/crj.13802
Circ_0028826 Promotes Growth and Metastasis of NSCLC via Acting as a Sponge of miR-758-3p to Derepress IDH2 Expression
Abstract
Background: Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is one of the cancers with the highest mortality and morbidity in the world. Circular RNAs (circRNAs) are newly identified players in carcinogenesis and development of various cancers. This study is aimed at exploring the functional effects and mechanism of circ_0028826 in the development of NSCLC.
Methods: Real-time quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) was used to detect the expression levels of circ_0028826, IDH2 mRNA, and miR-758-3p. IDH2, Bcl2, Bax, and E-cadherin protein levels were detected using a western blot. Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8), 5-ethynyl-2'-deoxyuridine (EdU), flow cytometry, wound healing, and transwell assays were used to assess the capacities of proliferation, apoptosis, migration, and invasion. Interaction between miR-758-3p and circ_0028826 or IDH2 was validated using a dual-luciferase reporter assay. The role of circ_0028826 in vivo was checked based on a xenograft tumor model.
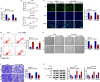
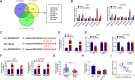
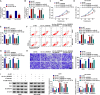
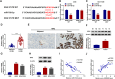
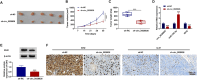
Results: Circ_0028826 was elevated in NSCLC, and its absence inhibited NSCLC cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and induced apoptosis. In terms of mechanism, circ_0028826 increased IDH2 expression by targeting miR-758-3p. In addition, circ_0028826 knockdown also regulated IDH2 by targeting miR-758-3p to inhibit tumor growth in vivo.
Conclusion: Circ_0028826 promoted the development of NSCLC via regulation of the miR-758-3p/IDH2 axis, providing a new strategy for NSCLC treatment.
Keywords: IDH2; NSCLC; circRNA; circ_0028826; miR‐758‐3p.
© 2024 The Author(s). The Clinical Respiratory Journal published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Wang S., Pan H., Liu D., et al., “Excision Repair Cross Complementation Group 1 Is a Chemotherapy‐Tolerating Gene in Cisplatin‐Based Treatment for Non‐Small Cell Lung Cancer,” International Journal of Oncology 46, no. 2 (2015): 809–817. - PubMed
-
- Reck M., Popat S., Reinmuth N., de Ruysscher D., Kerr K. M., and Peters S., “Metastatic Non‐small‐Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC): ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow‐Up,” Annals of Oncology 25 (2014): iii27–iii39. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

