Discovery of a novel highly specific, fully human PSCA antibody and its application as an antibody-drug conjugate in prostate cancer
- PMID: 39113562
- PMCID: PMC11312989
- DOI: 10.1080/19420862.2024.2387240
Discovery of a novel highly specific, fully human PSCA antibody and its application as an antibody-drug conjugate in prostate cancer
Abstract
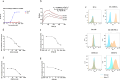
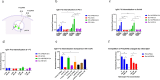
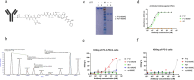
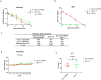
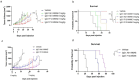
Prostate stem cell antigen (PSCA) is expressed in all stages of prostate cancer, including in advanced androgen-independent tumors and bone metastasis. PSCA may associate with prostate carcinogenesis and lineage plasticity in prostate cancer. PSCA is also a promising theranostic marker for a variety of other solid tumors, including pancreatic adenocarcinoma and renal cell carcinoma. Here, we identified a novel fully human PSCA antibody using phage display methodology. The structure-based affinity maturation yielded a high-affinity binder, F12, which is highly specific and does not bind to 6,000 human membrane proteins based on a membrane proteome array assay. F12 targets PSCA amino acids 63-69 as tested by the peptide scanning microarray, and it cross-reacts with the murine PSCA. IgG1 F12 efficiently internalizes into PSCA-expressing tumor cells. The antimitotic reagent monomethyl auristatin E (MMAE)-conjugated IgG1 F12 (ADC, F12-MMAE) exhibits dose-dependent efficacy and specificity in a human prostate cancer PC-3-PSCA xenograft NSG mouse model. This is a first reported ADC based on a fully human PSCA antibody and MMAE that is characterized in a xenograft murine model, which warrants further optimizations and investigations in additional preclinical tumor models, including prostate and other solid tumors.
Keywords: Antibody drug conjugate; PSCA; fully human antibody; monomethyl auristatin E; prostate cancer; tumor xenograft mouse model.
Conflict of interest statement
W.L., X.J.C., D.S.B., J.W.M., and D.S.D. are co-inventors of a patent, filed on May 2023 by the University of Pittsburgh, related to PSCA antibodies G7 and F12 described in this paper.escribed in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Baek D-S, Kim Y-J, Vergara S, Conard A, Adams C, Calero G, Ishima R, Mellors JW, Dimitrov DS. A highly-specific fully-human antibody and CAR-T cells targeting CD66e/CEACAM5 are cytotoxic for CD66e-expressing cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Lett. 2022;525:97–107. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2021.10.041. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
