Unlocking potential of oxytocin: improving intracranial lymphatic drainage for Alzheimer's disease treatment
- PMID: 39113801
- PMCID: PMC11303076
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.98587
Unlocking potential of oxytocin: improving intracranial lymphatic drainage for Alzheimer's disease treatment
Abstract
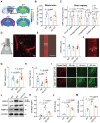
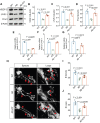
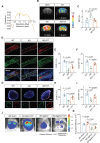
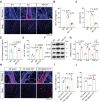
Background: The impediment to β-amyloid (Aβ) clearance caused by the invalid intracranial lymphatic drainage in Alzheimer's disease is pivotal to its pathogenesis, and finding reliable clinical available solutions to address this challenge remains elusive. Methods: The potential role and underlying mechanisms of intranasal oxytocin administration, an approved clinical intervention, in improving intracranial lymphatic drainage in middle-old-aged APP/PS1 mice were investigated by live mouse imaging, ASL/CEST-MRI scanning, in vivo two-photon imaging, immunofluorescence staining, ELISA, RT-qPCR, Western blotting, RNA-seq analysis, and cognitive behavioral tests. Results: Benefiting from multifaceted modulation of cerebral hemodynamics, aquaporin-4 polarization, meningeal lymphangiogenesis and transcriptional profiles, oxytocin administration normalized the structure and function of both the glymphatic and meningeal lymphatic systems severely impaired in middle-old-aged APP/PS1 mice. Consequently, this intervention facilitated the efficient drainage of Aβ from the brain parenchyma to the cerebrospinal fluid and then to the deep cervical lymph nodes for efficient clearance, as well as improvements in cognitive deficits. Conclusion: This work broadens the underlying neuroprotective mechanisms and clinical applications of oxytocin medication, showcasing its promising therapeutic prospects in central nervous system diseases with intracranial lymphatic dysfunction.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; Oxytocin; cerebral hemodynamics; intracranial lymphatic system; meningeal lymphangiogenesis; β-amyloid clearance.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures



References
-
- Sun BL, Wang LH, Yang T, Sun JY, Mao LL, Yang MF. et al. Lymphatic drainage system of the brain: A novel target for intervention of neurological diseases. Prog Neurobiol. 2018;163-164:118–43. - PubMed
-
- Chen J, Wang L, Xu H, Wang Y, Liang Q. The lymphatic drainage system of the CNS plays a role in lymphatic drainage, immunity, and neuroinflammation in stroke. J Leukoc Biol. 2021;110:283–91. - PubMed
-
- Bower NI, Hogan BM. Brain drains: new insights into brain clearance pathways from lymphatic biology. Journal of Molecular Medicine. 2018;96:383–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

