The predictive value of peripheral blood cell mitochondrial gene expression in identifying the prognosis in pediatric sepsis at preschool age
- PMID: 39113822
- PMCID: PMC11303305
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1413103
The predictive value of peripheral blood cell mitochondrial gene expression in identifying the prognosis in pediatric sepsis at preschool age
Abstract
Background: Sepsis represents a severe manifestation of infection often accompanied by metabolic disorders and mitochondrial dysfunction. Notably, mitochondrial DNA copy number (mtDNA-CN) and the expression of specific mitochondrial genes have emerged as sensitive indicators of mitochondrial function. To investigate the utility of mitochondrial gene expression in peripheral blood cells for distinguishing severe infections and predicting associated outcomes, we conducted a prospective cohort study.
Methods: We established a prospective cohort comprising 74 patients with non-sepsis pneumonia and 67 cases of sepsis induced by respiratory infections, aging from 2 to 6 years old. We documented corresponding clinical data and laboratory information and collected blood samples upon initial hospital admission. Peripheral blood cells were promptly isolated, and both total DNA and RNA were extracted. We utilized absolute quantification PCR to assess mtDNA-CN, as well as the expression levels of mt-CO1, mt-ND1, and mt-ATP6. Subsequently, we extended these comparisons to include survivors and non-survivors among patients with sepsis using univariate and multivariate analyses. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were constructed to assess the diagnostic potential.
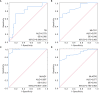
Results: The mtDNA-CN in peripheral blood cells was significantly lower in the sepsis group. Univariate analysis revealed a significant reduction in the expression of mt-CO1, mt-ND1, and mt-ATP6 in patients with sepsis. However, multivariate analysis did not support the use of mitochondrial function in peripheral blood cells for sepsis diagnosis. In the comparison between pediatric sepsis survivors and non-survivors, univariate analysis indicated a substantial reduction in the expression of mt-CO1, mt-ND1, and mt-ATP6 among non-survivors. Notably, total bilirubin (TB), mt-CO1, mt-ND1, and mt-ATP6 levels were identified as independent risk factors for sepsis-induced mortality. ROC curves were then established for these independent risk factors, revealing areas under the curve (AUCs) of 0.753 for TB (95% CI 0.596-0.910), 0.870 for mt-CO1 (95% CI 0.775-0.965), 0.987 for mt-ND1 (95% CI 0.964-1.000), and 0.877 for mt-ATP6 (95% CI 0.793-0.962).
Conclusion: MtDNA-CN and mitochondrial gene expression are closely linked to the severity and clinical outcomes of infectious diseases. Severe infections lead to impaired mitochondrial function in peripheral blood cells. Notably, when compared to other laboratory parameters, the expression levels of mt-CO1, mt-ND1, and mt-ATP6 demonstrate promising potential for assessing the prognosis of pediatric sepsis.
Keywords: MT-ATP6; MT-CO1; Mt-ND1; mitochondrial DNA copy number; prognosis; sepsis.
Copyright © 2024 Jing, Zhang, Zhao, Li and Wen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The mitochondrial DNA copy number of cumulus granulosa cells may be related to the maturity of oocyte cytoplasm.Hum Reprod. 2020 May 1;35(5):1120-1129. doi: 10.1093/humrep/deaa085. Hum Reprod. 2020. PMID: 32358599
-
Novel non-neutral mitochondrial DNA mutations found in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Clin Genet. 2018 Feb;93(2):275-285. doi: 10.1111/cge.13100. Epub 2017 Dec 20. Clin Genet. 2018. PMID: 28708239
-
Natural History of Patients With Mitochondrial ATPase Deficiency Due to Pathogenic Variants of MT-ATP6 and MT-ATP8.Neurology. 2025 Apr;104(7):e213462. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000213462. Epub 2025 Mar 20. Neurology. 2025. PMID: 40112238 Free PMC article.
-
MT-ATP6 mitochondrial disease variants: Phenotypic and biochemical features analysis in 218 published cases and cohort of 14 new cases.Hum Mutat. 2019 May;40(5):499-515. doi: 10.1002/humu.23723. Epub 2019 Mar 4. Hum Mutat. 2019. PMID: 30763462 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Variants in Human ATP Synthase Mitochondrial Genes: Biochemical Dysfunctions, Associated Diseases, and Therapies.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 13;25(4):2239. doi: 10.3390/ijms25042239. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38396915 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Autophagic Activity in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells of Critically Ill Patients With and Without Intensive Care Unit-Acquired Weakness: A Cross-Sectional Observational Study.Cureus. 2025 Apr 21;17(4):e82706. doi: 10.7759/cureus.82706. eCollection 2025 Apr. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40400839 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Busani S., De Biasi S., Nasi M., Paolini A., Venturelli S., Tosi M., et al. . (2020). Increased plasma levels of mitochondrial DNA and normal inflammasome gene expression in monocytes characterize patients with septic shock due to multidrug resistant bacteria. Front. Immunol. 11. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00768 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

